23 myths about cancer that you have always believed
You must stop believing these common misconceptions about cancer.

According to figures of theCenters for Disaster Control and Prevention (CDC), Cancer is the second cause of death in the United States. And yet, the general public is always relatively in the dark when it comes to information on the disease. What is worse is that so many misconceptions about the disease spread from far and both online and offering difficult for people to distinguishReal medical advice False grounds. We have gathered scientific evidence and expert medical advice to disperse the most common cancer myths once and for all.
1 Myth: Eating sugar will aggravate your cancer.

Made: Perhaps because the cancer cells consume more glucose than the other cells, people came to believe that the error of eating sugar will aggravate the disease. However, theNational Cancer Institute Disputes This claim, noting that "no study has shown that eating sugar will make your cancer worse or if you stop eating sugar, your cancer will decrease or disappear."
2 Myth: The more dairy, the more likely you are to get breast cancer.
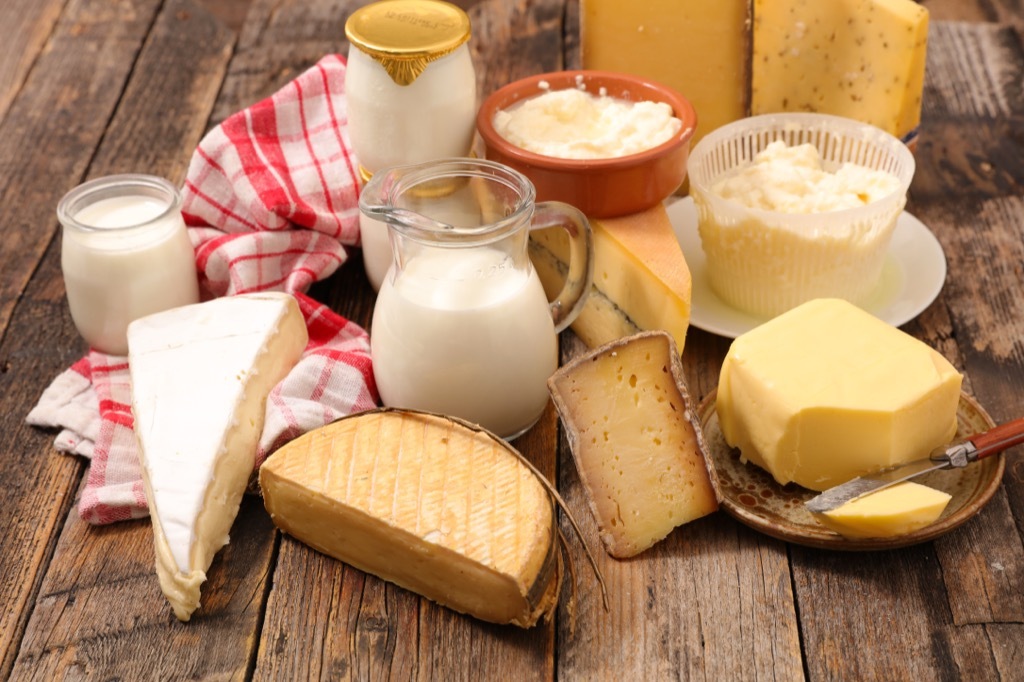

Made: No, you do not need to give up Parmesan cheese and yogurt parks to protect you from breast cancer. A pivotal study of 2002 published in theInternational newspaper of epidemiology It concluded that there is "no significant association between the contributions of ... Total dairy fluids or total dairy solids and the risk of breast cancer".
3 Myth: The consumption of artificial sweeteners causes cancer.

Made: People have become concerned in the 1970s and the 80s whenstudies Returned demonstrating that artificial sweeteners, such as saccharin and aspartame, could cause cancer in mice - but other tests have proved that these substances did not have the same effect in humans. Today, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) maintains that all these sugar substitutes (except cyclamate) are safe for consumption.
4 Myth: The use of a mobile phone can cause cancer.

MadeThis myth of common cancer stems from the fact that cell phones generate electromagnetic radiation. However, there is a difference between high frequency radiation (such as x-ray radiation) and low frequency rays (what cell phones emit).
Although high frequency radiation can increase your risk of cancer, there is no conclusive evidence that low frequency radiation have such an effect on the body. As a 2015 study ofScientific Committee on Emerging and Newly Identified Health Risks ONDA: "Epidemiological studies on the electromagnetic field exposure of mobile phones do not show an increased risk of brain tumors [and], they do not indicate an increased risk for other cancers".
5 Myth: Cancer is 100% hereditary.

Made: Although research is always made on theCauses of cancerThe National Cancer Institute puts the number of hereditary cancers from 5 to 10%. The remaining 90 to 95% of known cancers are the result of all exposure to harmful environmental agents such as tobaccoMutations of natural genes due to aging.
6 Myth: Only women can have breast cancer.

Made: Although much less common, it is possible that a man developsbreast cancer. According to the non-profit goalBreastscape.org, the average man has a chance of 1 out of 883 people to have a breast cancer of his life.
7 Myth: If a mammography comes up clean, there is no breast cancer.

Made: "Mammograms may be missed regarding the conclusions," saysJanie Grumley, MD, a mammary surgical occolor atCenter de la Providence Saint John in California. "If there is a breast symptom, a clear mammogram is not enough." She says that patients with breast cancer predisposition should especially look at MRI for more accurate screening.
8 Myth: dye your hair increases your risk of cancer.

Made: Studies on the incidence assignments of hair coloring have had conflicting results. Because of that, theInternational Agency for Cancer Research concluded that the use of hair coloring is "unclassifiable as to its carcinogenicity for man", although they aremadeNotify that "occupational exposures like hairdresser or hairstyle are probably carcinogenic for humans".
9 Myth: how much you weigh you has nothing to do with your risk of cancer.

Made: Unfortunately, your weight and risk of cancer are directly correlated. According to a 2015 study published inThe oncology lancet, about 3.6% of all new cancer cases in adults were related to the weight in 2012.
There are many possible explanations as to why obesity places people with a greater risk of cancer. We are that people who are overweight have oftenChronic inflammation of low level, which can damage the DNA over time and grow in the disease.
10 Myth: People with darker skin can not get skin cancer.

Made: Having a darker skin does not protect you from the perils of the sun. In fact, althoughskin cancer is more often seen in people with lighter skin, a 2014 study published in theJournal of the American Academy of Dermatology found that the disease is more fatal in people with darker skin tones.
In addition, some skin cancers - like an acral melanoma, the type that killedBob MarleyAt the relatively young age of 36 - are more often seen in people of color, so it is important toAlways apply a sunscreen before going out.
11 Myth: Use an antiperspirant causes breast cancer.

Made: Does the deodorant provoke breast cancer? The short answer is no. This myth was created online as a rumor that the substances of the antiperspirants could infiltrate the lymphatic nodes into the armpit and mutation cells to cause cancer. However, theAmerican Cancer Society Reduces this claim, noting that there are "very little scientific evidence" to safeguard this scientific hypothesis.
And during the comparison of 813 women with the disease and 793 women without her, a noticeable study of 2002 published in theJournal of the National Cancer Institute found that there was no link between the risk of breast cancer and antiperspirant use, the deodorant use or shaving of the armpits.
12 Myth: Breast implants increase your risk of breast cancer.

Made: A significant 2001 meta-analysis published in the journalPlastic and reconstructive surgery Concluded that "breast implants do not pose any additional risk of breast cancer," there is no reason to be afraid to get breast implants if that's what you want. However, it is important to note that there seems to be aVery small link Between implants and a rare type of treatable cancer called lamphoma with large anaplastic cell. Just something to conscience!
13 Myth: People treated for cancer must stay in the hospital.
Made: Although the treatment of cancer involves several trips to the hospital, you must not stay there until you have a remission. In fact, many people with cancer at the beginning of the first stages are able to continue to live their lives, at the hospital only for treatments and checkups.
14 Myth: Only cigarette smokers can have lung cancer.

Made: Although it is true that people who smoke areUp to 30 times more likely To obtain lung cancer, those who are not at risk also through other things such as second-hand smoke, radon in the air and asbestos exposure.
15 Myth: If you have HPV, you will definitely get cervical cancer.

Made: Some strains of human papillomavirus or HPV, develop cervical cancer over time, but not always. According toAmerican Association of Sexual Health, about 14 million new HPV cases take place every year in the United States, but earlier this year, theAmerican Society of Clinical Oncology Estimation of a number of women relatively less than 13,170 women will have a diagnosis of cervical cancer.
16 Myth: Have a bad attitude will make your cancer worse.

Made: Often, when a person with cancer does not see any improvement, their instinct is to blame and their negative attitude like the root of the problem. However, theAmerican Cancer SocietyNote that there does not seem to be a link between personality traits and cancer survival rates. "On the basis of what we now know about how cancer begins and develops, there is no reason to believe that emotions can cause cancer or help it develop", note-T- he on their website.
17 Myth: Having a surgery causes a propagation of cancer.
Made: "There is no evidence to support the idea that ... surgery causes the propagation of cancer," says theCANCER CANCER NSW. Because the disease develops and multiplies entirely through blood, there is no way that surgery would do worse.
18 Myth: Herbal supplements can cure cancer.

Made: Herbal supplements can help put a person with cancer on the path of remission, but only when used in combination with conventional treatments, according to a 2013 study in the newspaper.Complementary and alternative medicine based on evidence. However, since some supplements likeSaint Jean Interact badly with traditional drugs, it is important to let your doctor know which herbal remedies you want to try before starting a new experimental regime.
19 Myth: Air exposure will cause cancer propagation.
Made: Because many people come out of biopsies feel worse than they did, a common myth of the cancer community is that cancer exposure in the air will prevail. However, as authorsJamie SchwachterandJosette Snyder noted in their bookThe Complete Cancer Organizer, "There is no factual evidence that suggests that a biopsy of a lesion can lead to a propagation of cancer, nor a suggested evidence to suggest that ... the exposure of a tumor to air can lead to a Propagation of cancer to other parts of the body. "
20 Myth: Chemotherapy always feels sick.

Made: The treatment of chemotherapy has become long since its first use in the 1940s and 50 years. "We have a lot of good things we do to reduce or even eliminate many of these side effects"Issam Alawin, MD, a medical oncologist at the tulsa branch of theCancer treatment centers of America, explained on the organization's website.
21 Myth: Cancer is contagious.

Made: As theAmerican Cancer Society Notes, cancer itself is not contagious and you can not contract someone else's disease that has. However, there issome contagious viruses This can cause cancer to be careful. HPV and hepatitis B and C are contagious and can cause cancer on the line.
22 Myth: Fluoride can cause cancer.

Made: Despite what conspiracy theorists believe in water supply, fluorine, which can be found in all, supplement toothpaste - does not cause cancer. In February 1991, theDepartment of Health and Human Services Examined more than 50 human population studies and stated that the natural substance "does not pose a risk of detectable cancer for humans".
23 Myth: Cancer is a death penalty.

Made: Thanks to technological advances and medical discoveries, the chances of living with cancer are much better than they used to be. According to the National Cancer Institute, the five-year survival rate for all types of combined cancers is about 67% and that statistics are as high as 90% for specific cancers such as breast, prostate and thyroid .

The best 7 Latin American fashion designers of all time