These are the parts of the body that you have not even known that you had had
You are literally more than met with the eye.
We all know our "heads, shoulders, knees and toes". But what about our plantaris, long and early palmaris? No, these are not composed of words ofHarry Potter Wherethe Lord of the Rings. These are parts of the actual body.
Yes, for most of us, the body welcomes a lot of secrets. Some, you may have seen and just not registered as his own thing. (Exposure A: This strange tendon in your wrist.) But others, like a previously uncovered corneal layer, are totally new and elusive. So, without any other teen, here is a break of most of the most famous body pieces. Whether due to their size, in use or indeterminacy, these parts of the body have escaped the written knowledge too long.
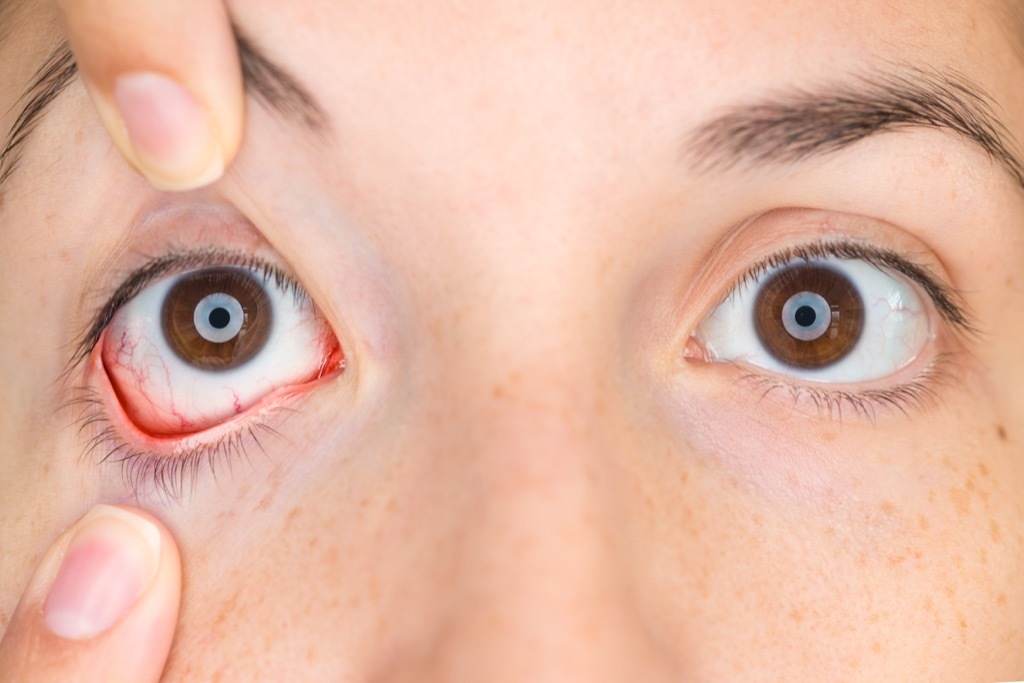
1 Lacrimal punctum
Known in the heart of the "eyelid", it is a small cavity located at the bottom and upper corner of your eyelids that can be found if you look closely. Although everyone has one, the hole can vary in size depending on the person. According toCleveland Clinic, its use is to help drain some of the surpluses of your eye on the tears of your eye, channeling it at the back of your nose (hence therunny nose when you cry). In some cases, Puncta LACCRIM can malfunction and work upside down, allowing individuals to squirt liquids from their eyes. EW.
2 Jacobson's organ
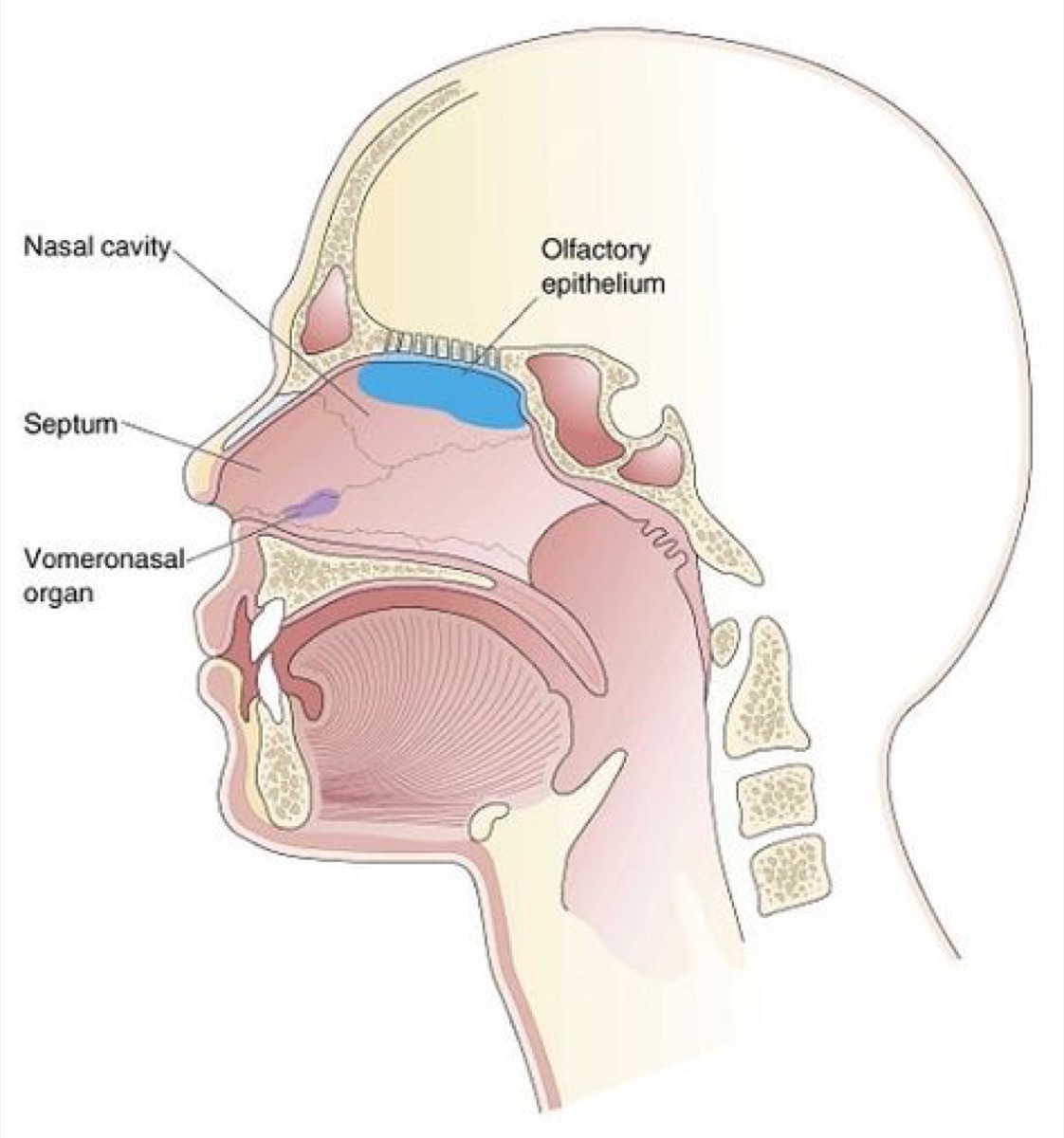
Also called thevomeronasal organThis organ is a group of sensory cells found in the main nasal chamber of most amphibians, reptiles and mammals. Hisuse is to detect moisture odors such aspheromones to communicate non-verbally, in particular in the field of romance and sexuality. Due to a lack of adequate receptors in humans, however, the organ istook into consideration By most to be non-functional, a remnant of once earlier.
3 THE MESENTE
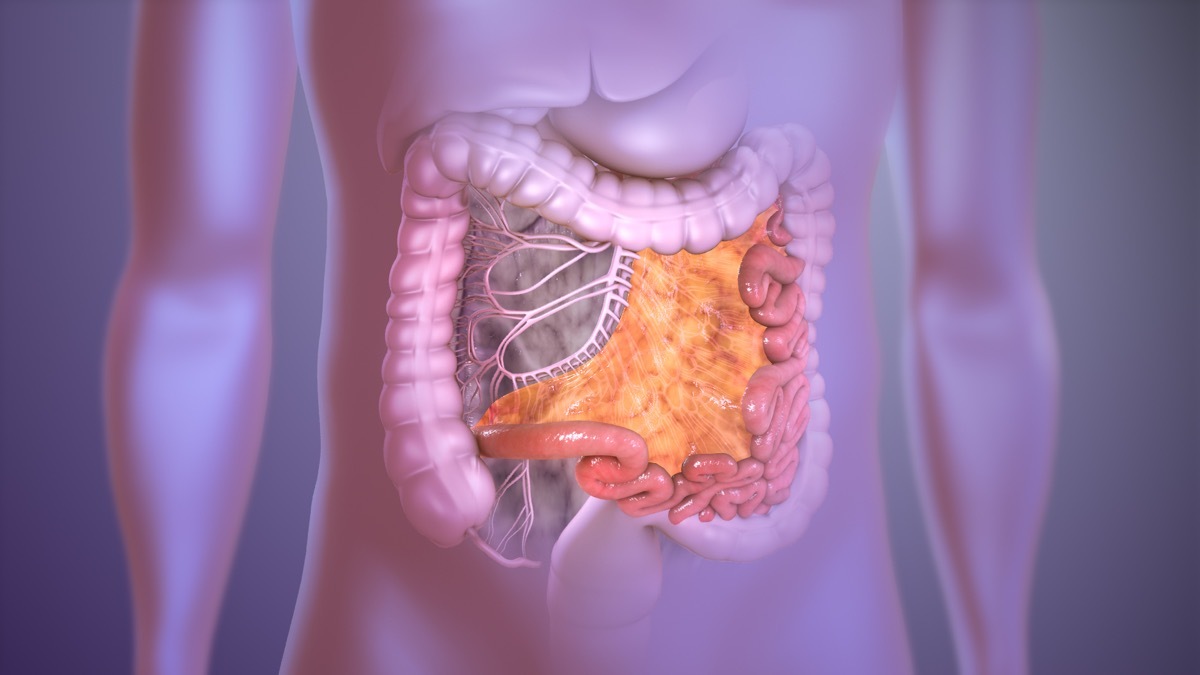
The Mesenty is a cloth fold located in the intestine that connects the stomach, the intestines, the pancreas, the spleen and other internal organs to the abdomen. Until recently, however, the Mesenty was considered a collection of disparate membranes. It was not before the publication of the research in 2016 inThe lancet that it has been considered a continuous and continuous organ. As a result, additional research on the still largely unknown body should be coming in the near future.
4 Philant
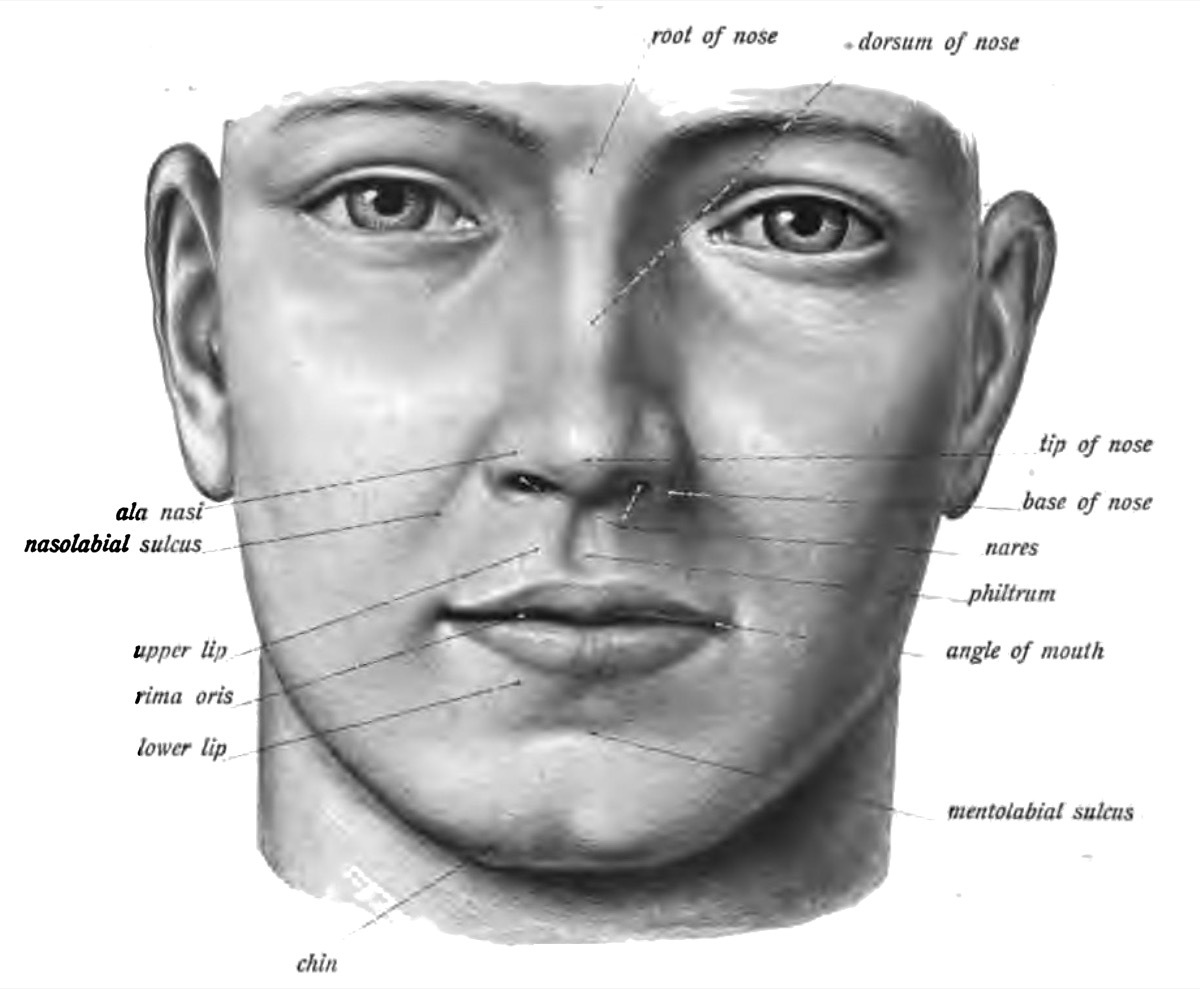
In most mammals -like your dog-The philtrum is a tiny slit near the nose thatallow The odor molecules collected on the nose to filter either in the mouth or in the aforementioned vomeronase member. In humans, however, the philtrum hasceased Play such a role, and remains just like cute groove withdrawal between your nose and your mouth. An abnormal philtrum, meanwhile,can report the presence of autism or fetal alcohol syndrome.
5 Auricle muscles
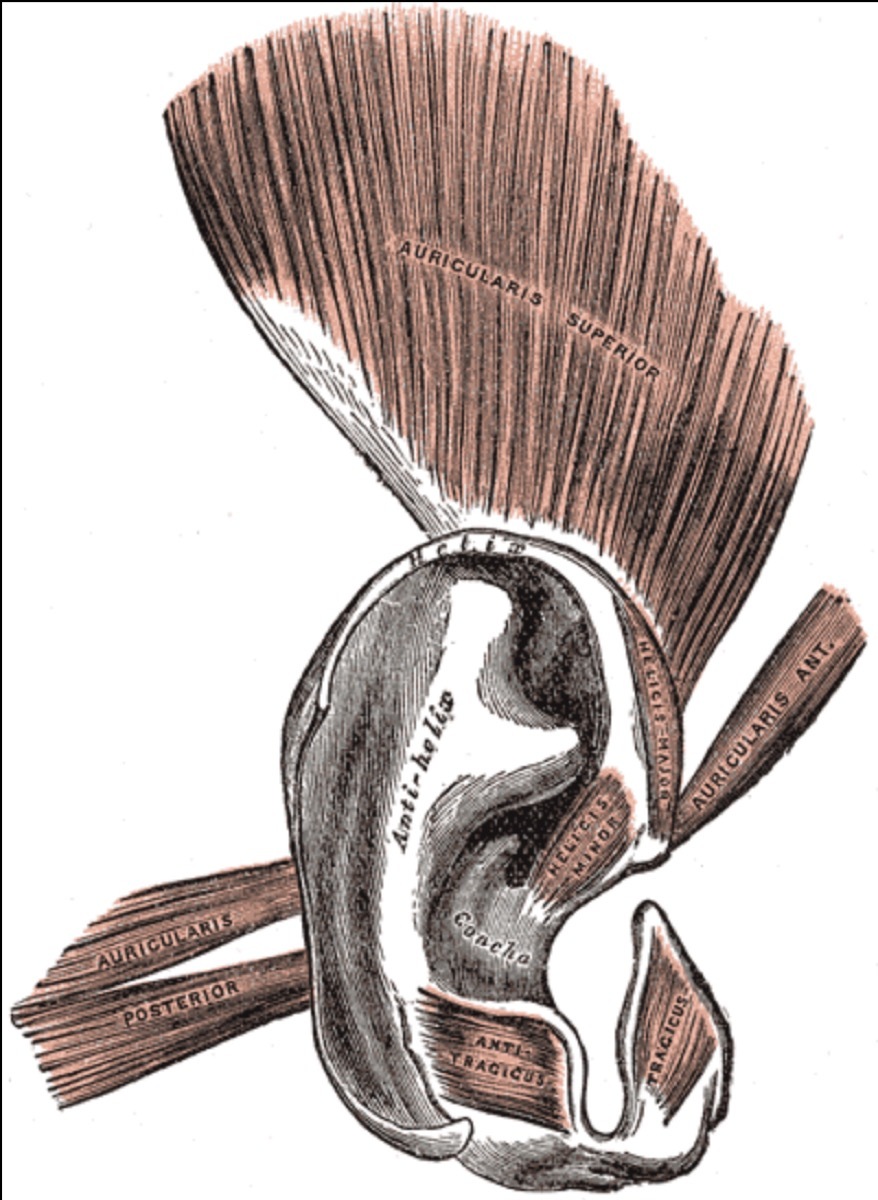
TheAuricle muscles are a collection of three little known musclesoutside the ear. During other mammals, these muscles can be used to tilt the ear to sounds of interest, humans have largely ceased to use them. Instead, they simply turn his head. Some people can, however, have their operation - offering an excellent lounge trick for years to come.
6 The long palmaris
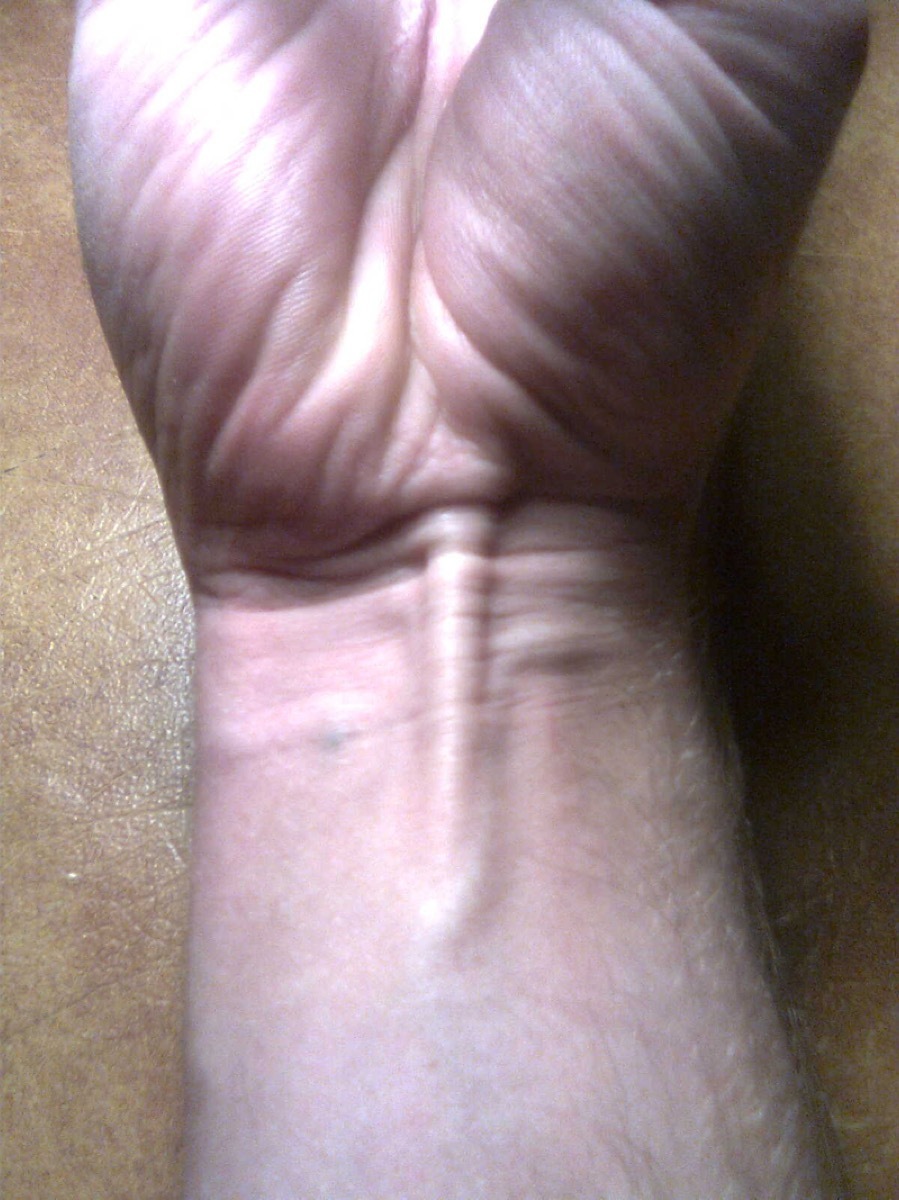
The long palmaris tendon is a thin muscle found in the middle of the wrist. Whilenumerous Remote parents of mammals, such as Oranguutan, always use the muscle, it has become vestigial both in humans and our more closest to the brothers of primates such as chimpanzee. As a result, it is really absent in about 15% of the population. To say if you have one or not, pinch your fourth finger to your thumb and flex your wrist. If present, a vertical line will take place under the skin. Fortunately, it's an absenceappear have little effect on the ability to join.
7 DUA layer

Discovered in 2013, the DUA layer is a membrane layer previously unknown on the cornea. Estimated at about 15 micrometers thick and elongated between two well known corneal layers, the DUA layer is known to be surprisingly strong and to emit a "a pretty sound of jump enough" when it bursts, according toThe examination of optometry.
His name, meanwhile, comes from the man who discovered it: Dr. Harminer Singh Dua from the University of Nottingham, cited at the time of the discovery - a quote he denies now - as saying that the result of its conclusions, "textbooks will literally be rewritten."
8 The muscle Arcto Pili (or "goose bums")

The pulp muscle of the arrooror is a small muscle at the base of each hair follicle that connects it to the skin tissue.When you get goose bumps, or do you have that your hair stands at the end of the excitement or cold, for example, this is due to the Piloci Arctorel muscle contracts, which makes the Bretect Foll, according toJohns Hopkins. According to a study inPsychophysiologyMeanwhile, in some humans, this muscle can actually be controlled, which allows them to evoke ear bumps on demand.
9 Plantaris
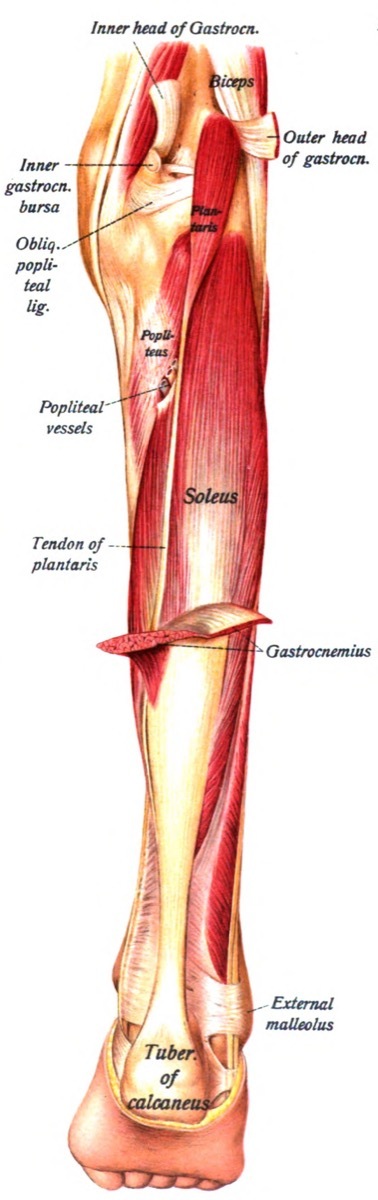
Plantaris is a thin muscle pencil flowing along the back of the leg. You probably never heard of that, however, because it is considered "little importance", according to the research published in theInternational Journal of Physiology.
In fact, according to theCanadian Chiropractic AssociationThis vestigial muscle is lacking, by some estimates, 20% of the population. Although its breakage is sometimes considered the cause of the "tennis leg", this prognosis has been strongly debated and is currently doing doubts. Thus, Plantaria is also discreet as ever.
10 Shiny
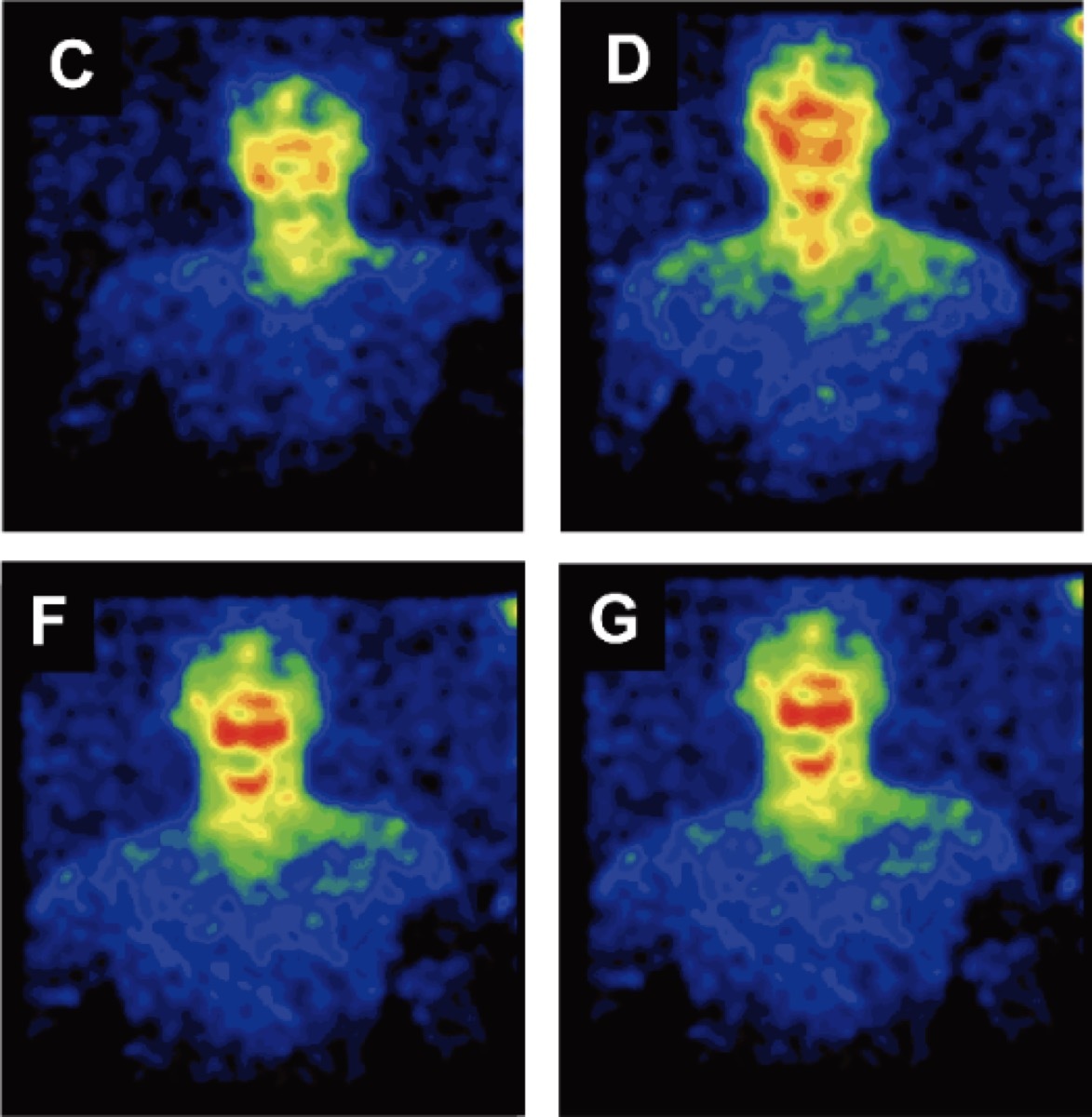
A little likesea fish, the human body really shines. According to the search published inPlos a, Your skin emits a light of about 1,000 times lower than the sensitivity required for our view. Interesting, the rhythm and intensity of the light were probably linked toChanges in metabolism, said the researchers of the study.
11 A tail
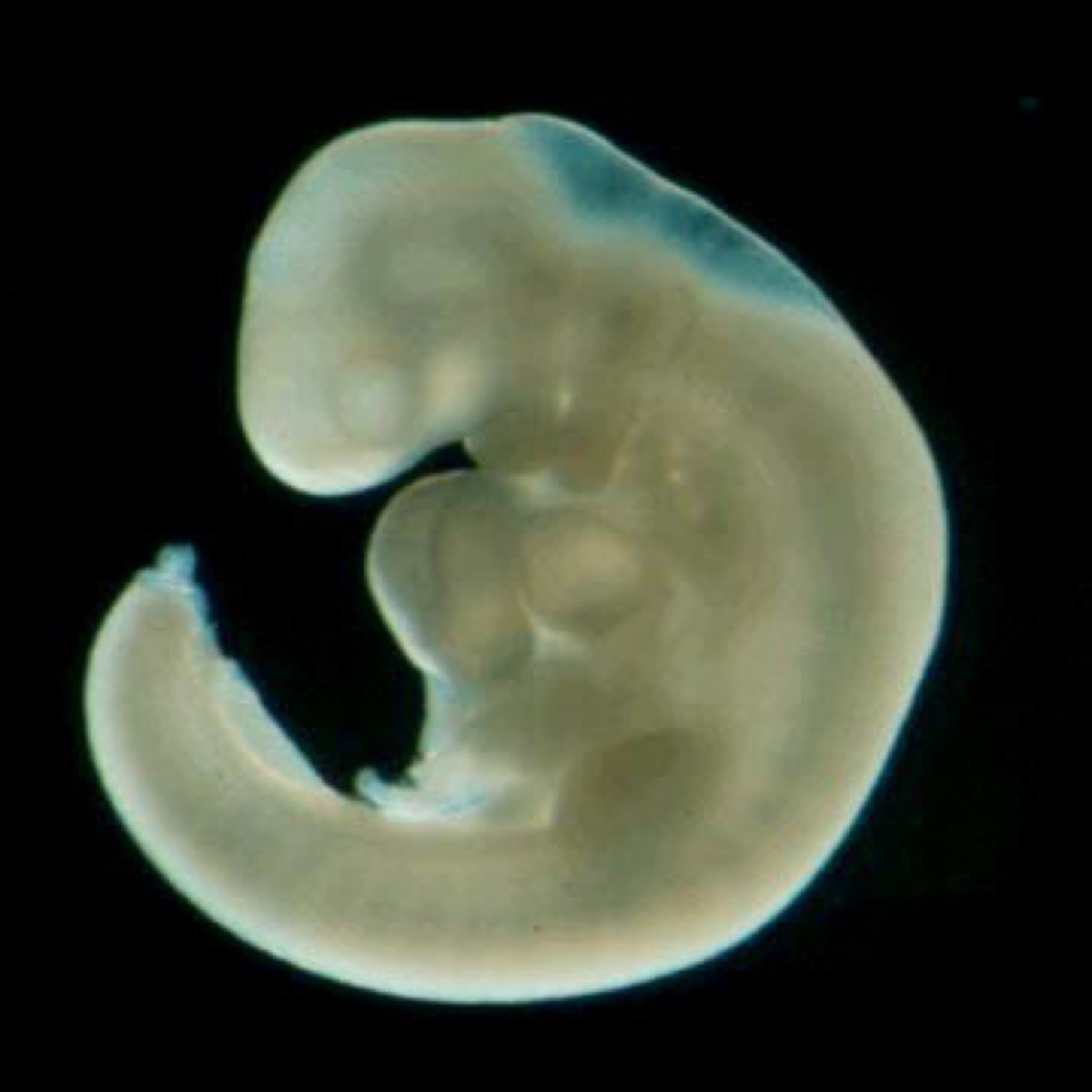
No need to look behind you - yours is probably left now. But in the sixth week of gestation, according toBerkeley University, most human embryos have a tail, which ends up disappearing when the fuse of vertebrae. There are, however, cases in which he remained, as published in theJournal of the Indian Association of Pediatric Surgeons. And for more human biology always fascinating, here is20 ways our bodies will be different in 100 years.
To discover more incredible secrets about the life of your best life,Click hereTo follow you on Instagram!


