To discover more incredible secrets about the life of your best life,Click hereTo follow you on Instagram!
25 things that would arrive at the planet if the population continues to grow
Spoiler alert: It does not look good.

The world's continuing balloon population. October 2011 in mid-2015 alone, the planet won some 300 million people and theThe United Nations (UN) projects that the population will reach 9.7 billion people by 2050.
This growth shows no sign of slowing down, but the potential effects of overpopulation are disastrous. More and more people means fewer resources and fewer resources, which would create a lot of economy andhealth crises. Keep reading to find out what could happen to the planet if the UN projection turns out to be true.
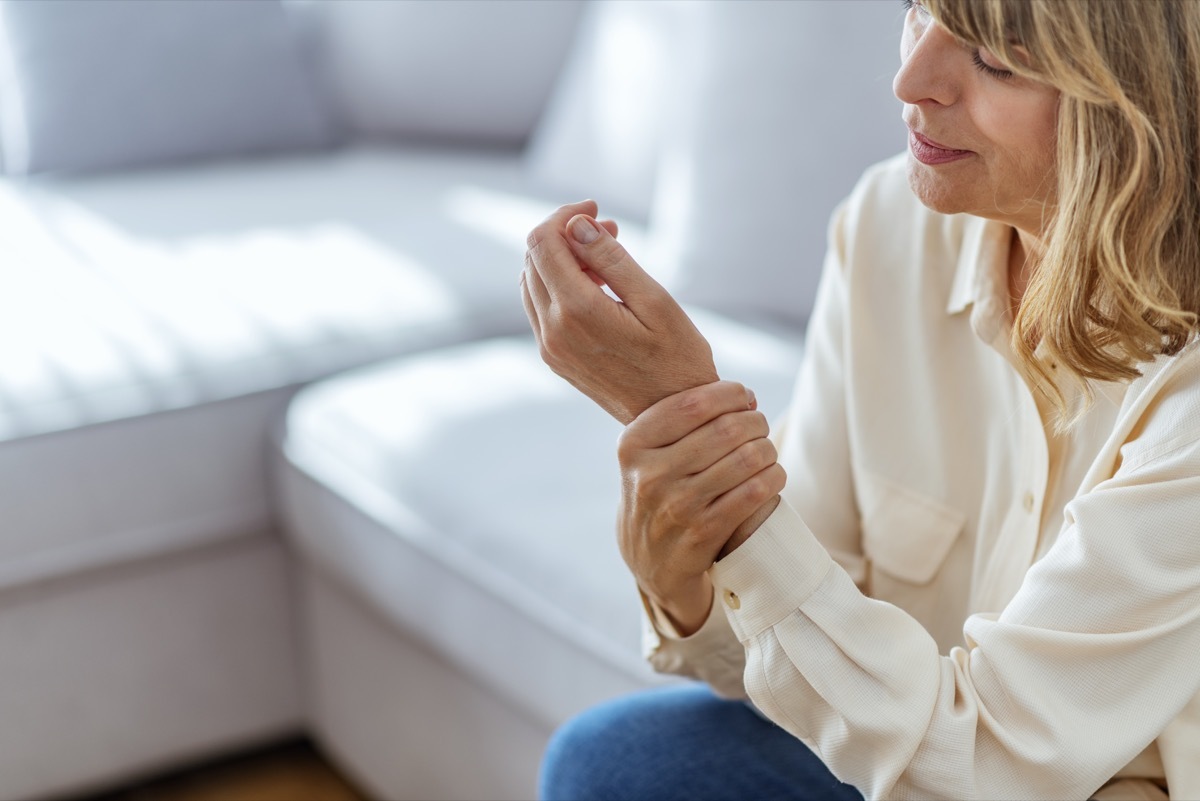
1 Increase in respiratory disease rates

The increase in air pollution that a larger population would inevitably cause the cause could possibly lead to an increase in respiratory diseases and asthma. An analysis of 2014 published inThe lancet Journal found that, in general, exposure to pollution "can contribute to asthma new appearance in children and adults" and "increase the risk of exacerbation of asthma symptoms".
2 More lung cancer and bladder
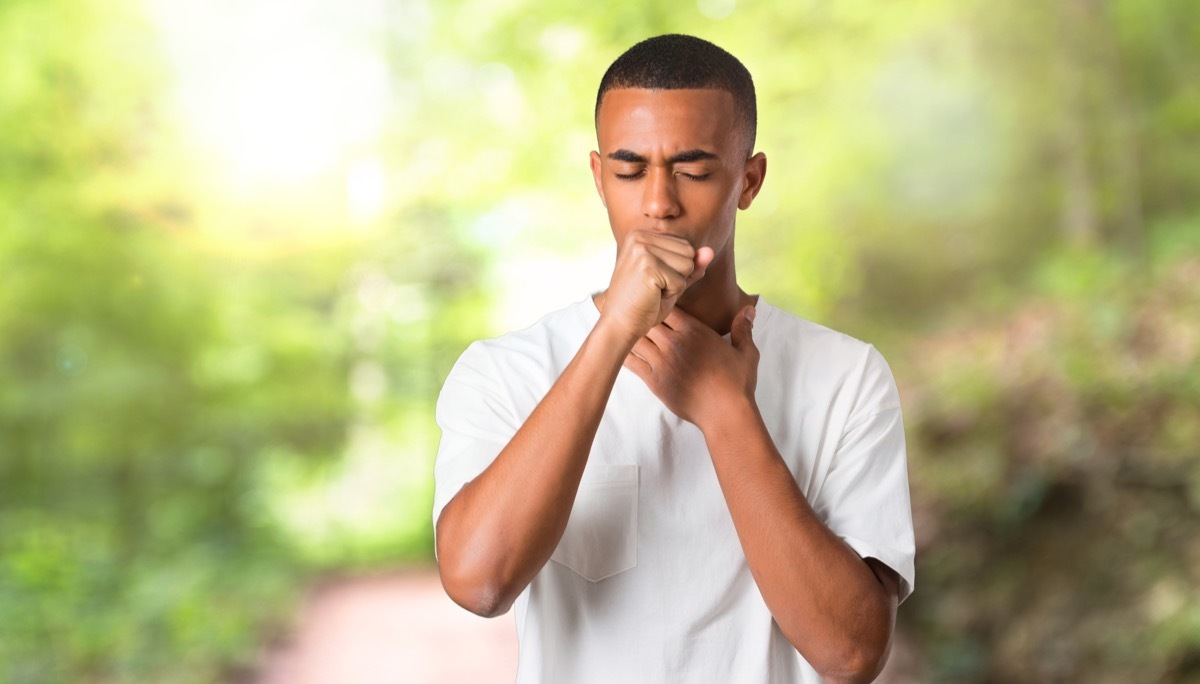

Air pollution is only causing asthma. RatherInternational Agency for Cancer Research (IARC) Outdoor air pollution recently classified as agent causing cancer after conclusive lung cancer and bladder cancer.
3 And more skin cancer
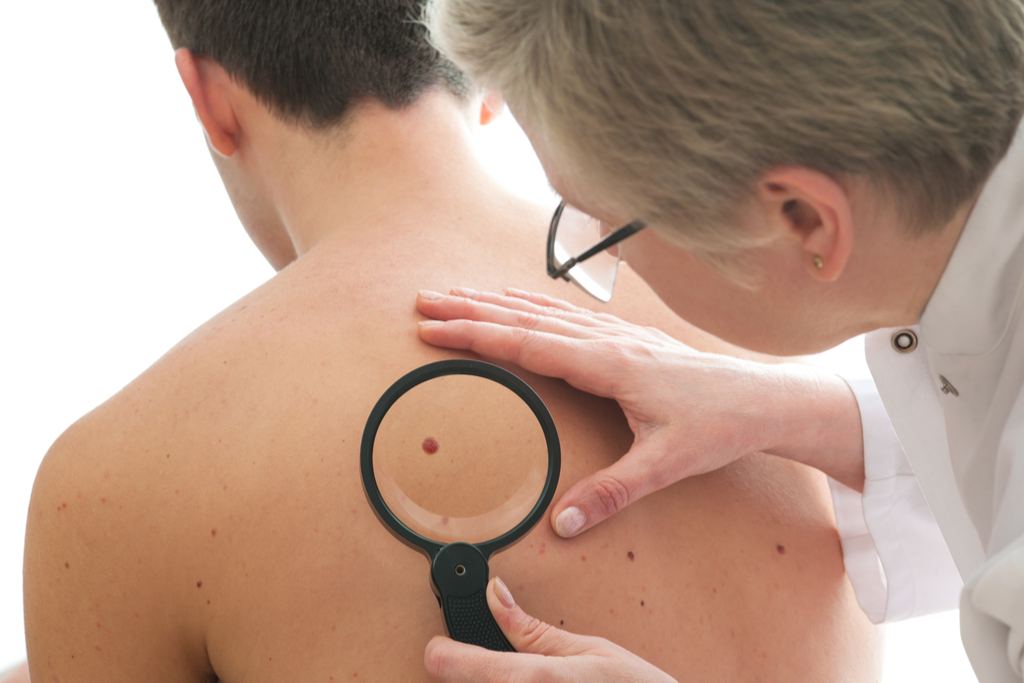
As atmospheric pollution is growing due to a rapidly growing population, it will also cause exhaustion of the ozone layer. And likeDr. Jayakanth M. J., a consultant at the Apollo Clinic in India,to explain, increased pollution exhausts the ozone layer, which in turn means that it "no longer protects us from the harmful ultraviolet rays (UV) of the sun causing skin problems such ascutaneous cancers and premature aging of the skin. "
4 Proliferation of infectious diseases

Viruses propagate more easily when people are confined to farm neighborhoods. In fact, according to theWorld Health Organization (WHO), "Insufficient shelter and overcrowding are major factors in the transmission of diseases with an epidemic potential." If the population should continue to grow at an alarming rate, needless to say that people will end up with a much less personal space and a much higher risk of contracting deadly diseases such as meningitis, typhus, cholera, etc.
5 Submerged and overcrowded hospitals
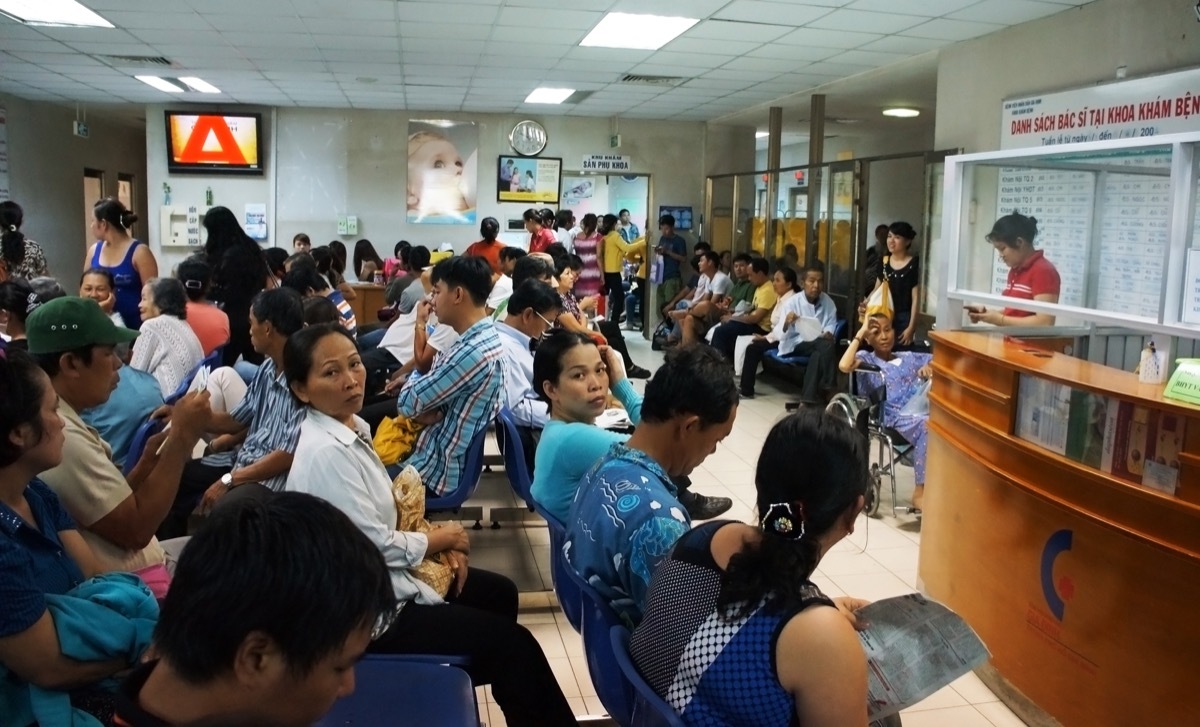

As we have seen after many natural disasters, the combination of too many people and not enough medical resources can create a dangerous situation. WHO notes that when you suffer from overcrowding, "public structures such as health facilities represent not only a concentrated area of patients but also a concentrated area of germs". In other words, a wider population could mean a deferred treatment for those who need it and the greatest spread of diseases.
6 Higher HIV / AIDS rate
Organization of public policiesInternational population action Writes that "there are often overlap between countries with juvenile populations, high levels of HIV prevalence and low access to family planning". In Swaziland, for example, 69,000 children were orphaned by AIDS and the country was strongly affected by AIDS-related deaths among adults of working age. "Given what scientists have observed in modern societies, an increase in the size of the population combined with a shortage of medical care and supplies could easily cause another HIV / AIDS epidemic.
7 More natural distassiaries

What is overpopulation and natural disasters have to do with each other? Not much, apparently. The more carbon dioxide in the environment, the more probably there are major natural disasters such as hurricanes. In the bookEnvironmental problems around human overpopulationResearchers noted that in India, "overpopulation makes the country subject to natural disasters" like tsunamis.
8 Exacerbated climate change

Although global climate change is already aggravated by the minute, increasing the number of people on the planet will only intensify the problem. A 2009 study published in the journalGlobal environmental change Analyzed the environmental impact of having children and found that in the United States, every child has added 9,441 metric tons of carbon dioxide to their legacy. (This represents 5.7 times more than average life emissions of 1,644 metric tonnes.)
9 Extinction of mass and animal plants

If and when overloaded cities are extending to welcome additional persons, many will be forced to overflow in areas that had already been intact. The problem? According toNational Federation of Wildlife, this expansion is estimated to give theextinction up to a third of the world's plant andanimal species.
10 Deforestation
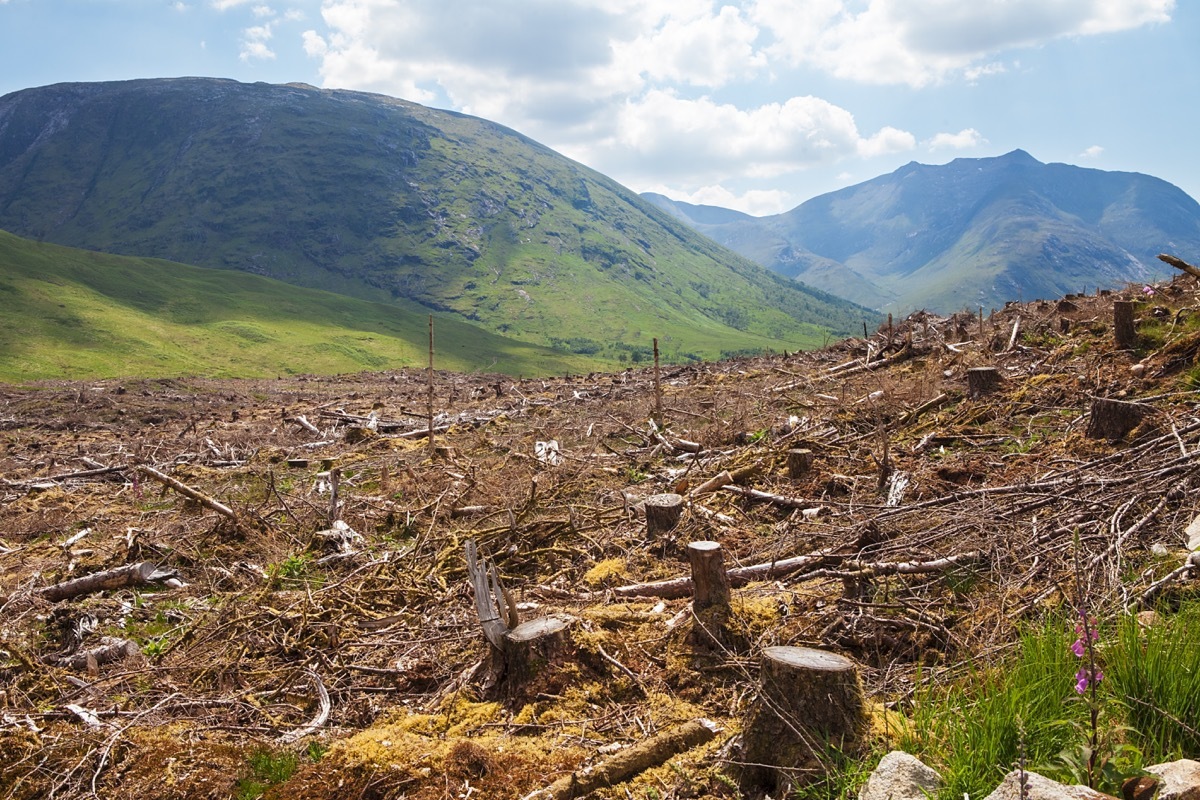

As a researcher on the environmental studies of the Swatthmore CollegeMax Katz-Balmes Explain: "overpopulation affects deforestation on a truly global scale, even in relatively uninhabited areas." According to Katz-Balmes, "a clear correlation exists between an extremely low population density and a forest maintenance". In other words, the more population increases, the worst deforestation will become.
11 Miserable in the morning of the switches
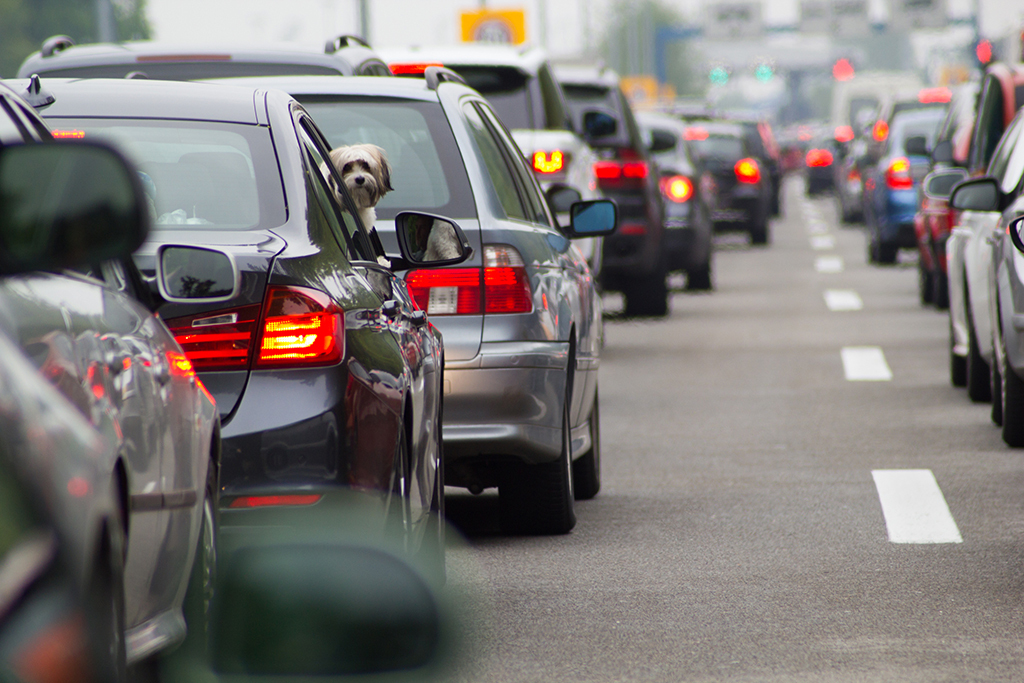

Sure,Horrible traffic would be one of the most immediate results of too many people. Although infrastructure improvements would eventually help mitigate some congestion, the number of cars fulfilling highways and roads would mean that places would take a lot more time. If you live in aMetropolitan area As New York or Los Angeles, it's probably difficult to imagine that aggravating traffic, but believe us when we say it's possible.
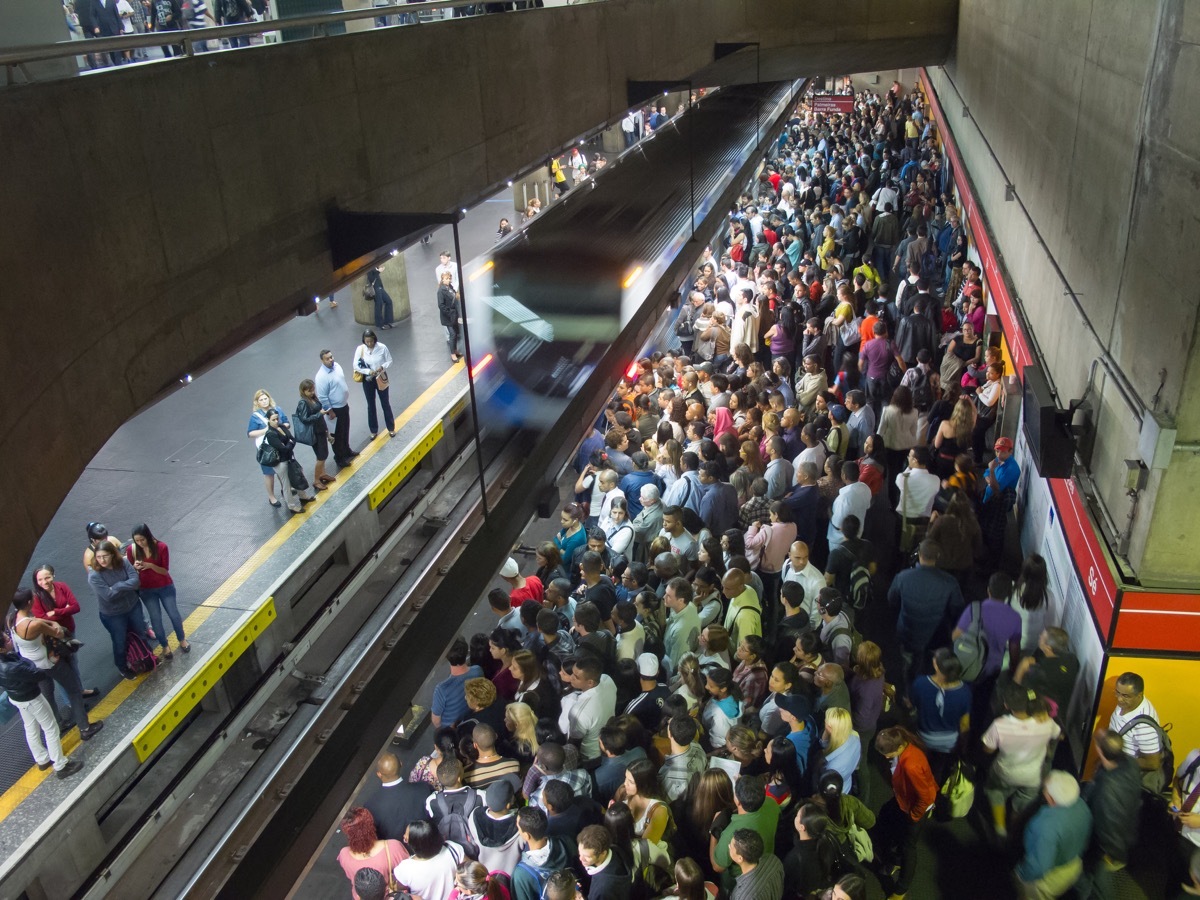
12 Overcrowded public transport
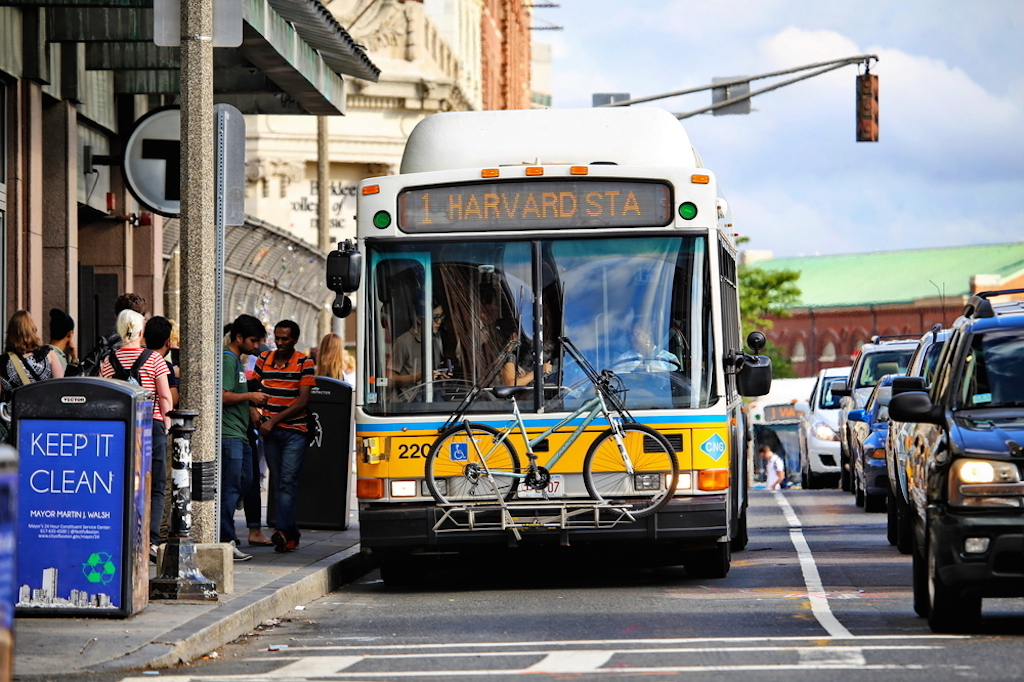

Do not think thatyour trip Will be a breeze in 30 years, just because you take the metro at work. A growing population would also put a huge pressure on metro, buses and other transit modes. Main cities in New York toMelbourne Already fighting to follow their customers and that it would only worse if the population predictions become reality.
13 Flamboyant food prices
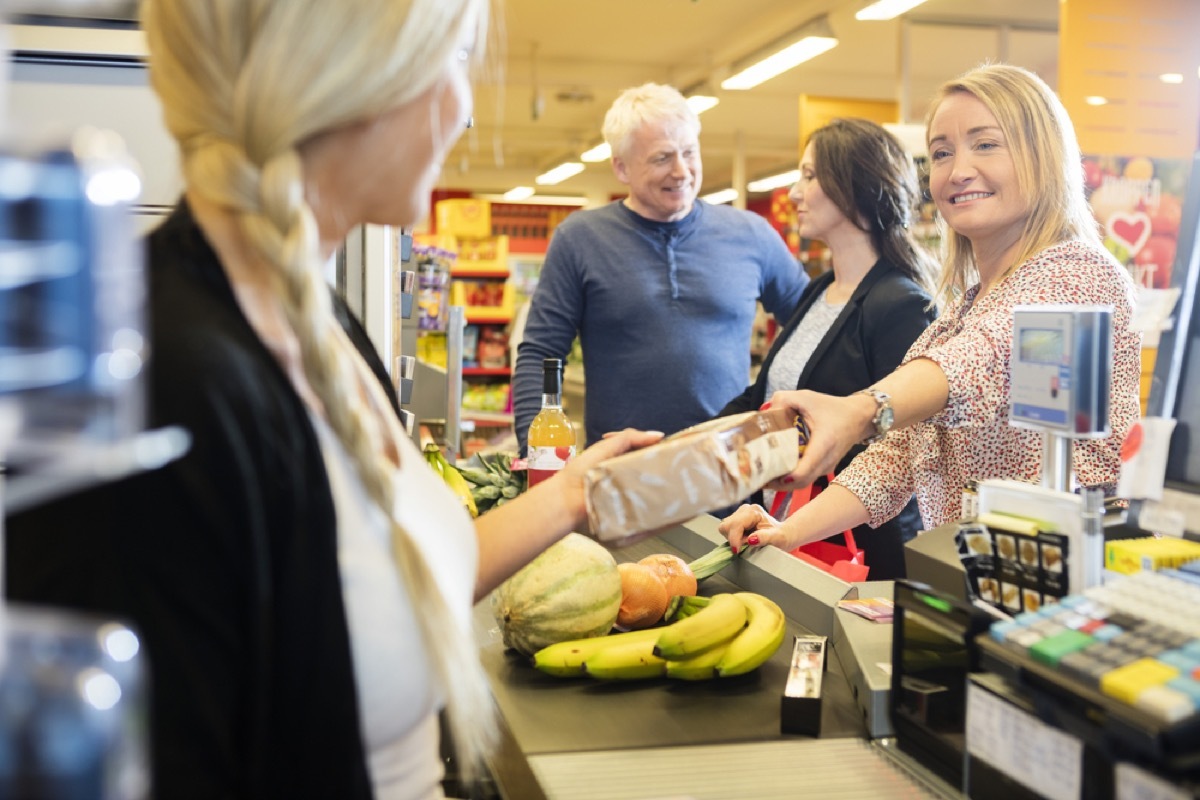

TheOrganization for food and agriculture (FAO) projects that food production must increase by 70% by 2050 to keep pace with increasing demand - but if the world's population has difficulty feeding, it is unlikely that it can stay satisfied for about 30 years. If production can not support the growing number of people, overpopulation could potentially result in an increase in food prices.
14 Food shortages

High food prices, frankly, are a good deal scenario. The worst case is a lack of food entirely. According to the public health resourceMPH online, one in eight across the world suffered from hunger or undernourishment between 2010 and 2012. This felt mainly in overcrowded parts of the world where demand ends the supply of food - and it does not will aggravate only when the population grows.
15 Tensive

When the population grows, it will need something to maintain it, namely protein-rich foods like fish. But asDermot O'Gorman, the CEO of World Wildlife Fund Australia,writing"Within 15 years, 115,000 tonnes of additional fish will be needed in the Pacific to provide livelihood communities and proteins they need."
16 Surprising

The need to produce more food for a larger population would put pressure on local and commercial farms. This could lead to intensive plant consumption by livestock, otherwise known assurprising. The lack of rotation of pasture animals combined with their over-consumption of natural resources would degrade the soil and would result in a range of other environmental problems.
17 Increase in agricultural runoff

A thrust for more food - and therefore, more breeding, inevitably leads to an increase in agricultural runoff. This, in turn, would pollute the water supplies of the world with things like "sediments, nutrients, pathogens, pesticides, metals and salts," according to theEnvironmental Protection Agency (EPA). And the last thing this planet needs is to pollute the fresh water it has.
18 Severely polluted water body
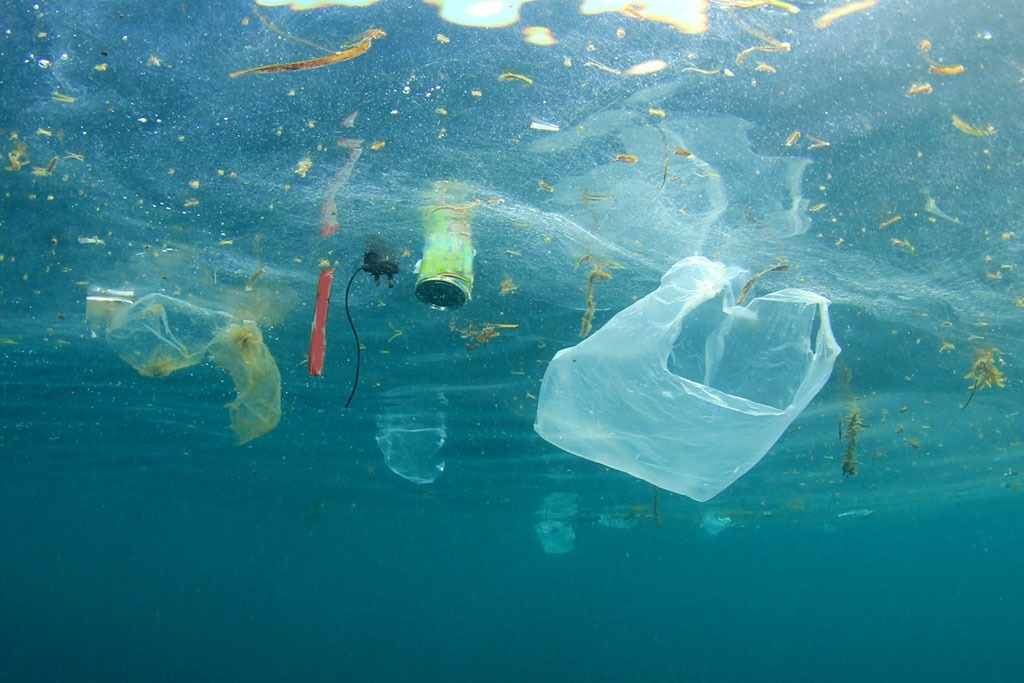

A larger population would threaten the sustainability of water supply in the world. As 2017 article published in the newspaperDurability Notes, "Human activities pose an important threat to river water quality when pollution exceeds the threshold limit", especially in urban areas that tend to grow at a much faster pace.
19 Water shortage
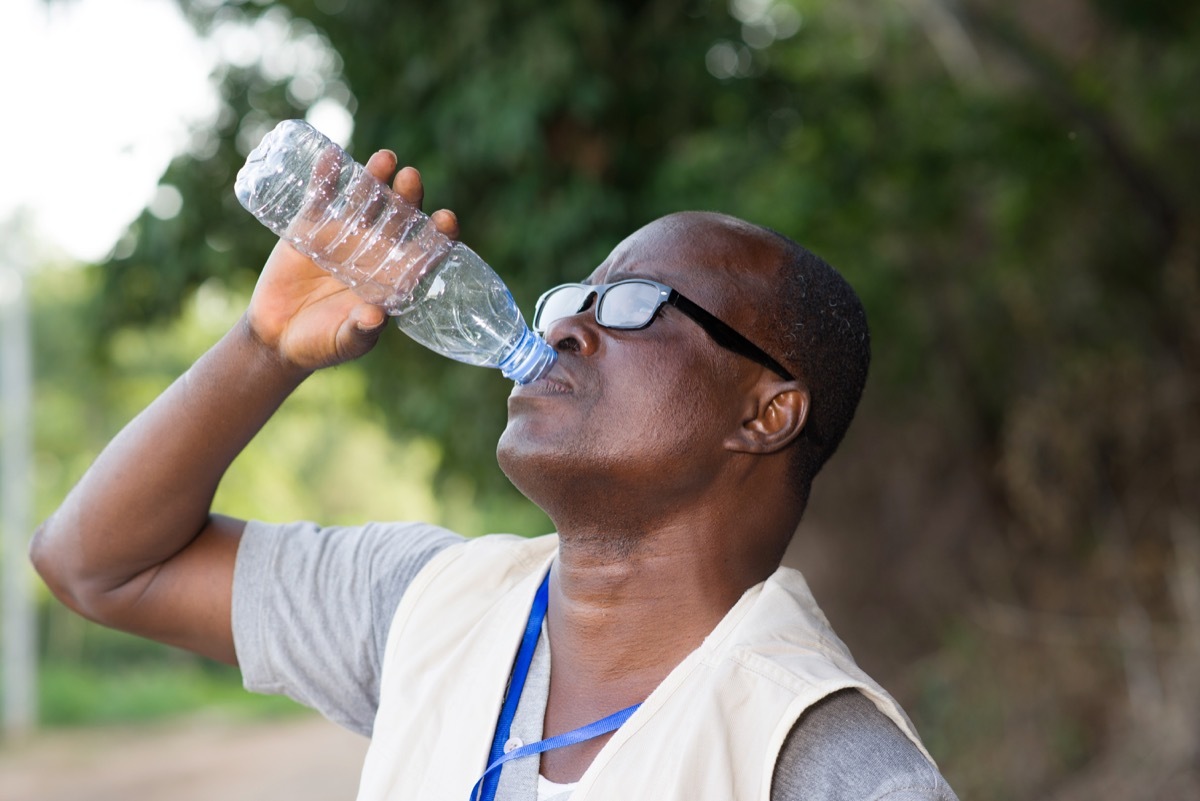

Although an overwhelming majority of the planet being water, only a limited amount of this water is actually fresh water that can be consumed. In addition, the population at its current size is already facing problems related to the scarcity of water: according to theWildlife World FundAbout 1.1 billion people currently lack access to water and 2.7 billion people have a limited amount of water available for at least one month of the year.
20 Desertification
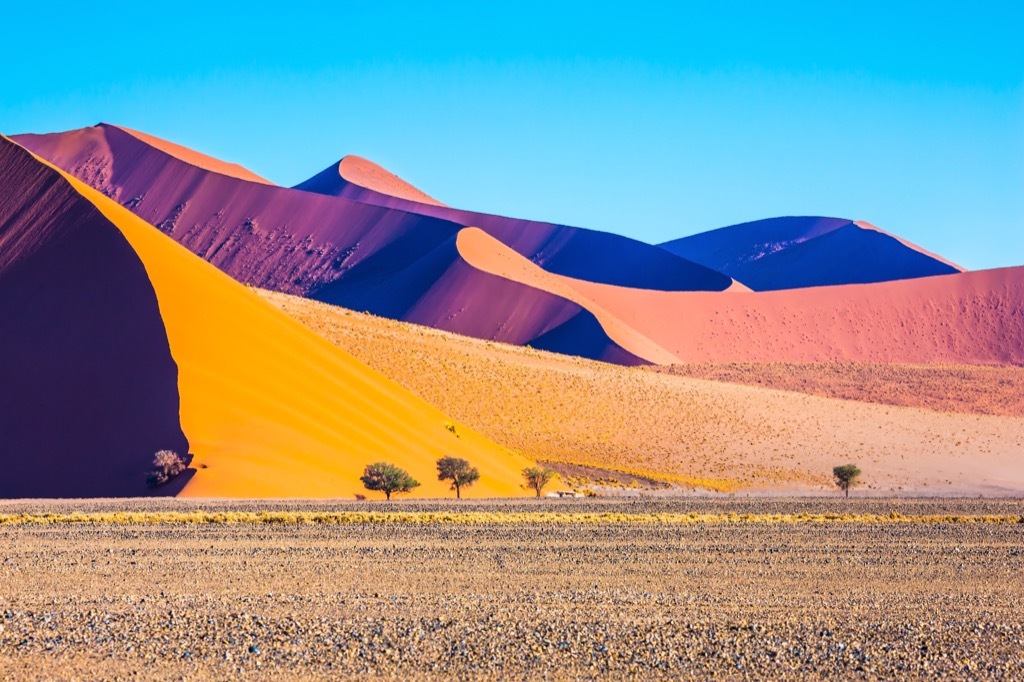

When dry earth is overused for culture or other purposes, this eventually leads to desertification. According toInternational Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentDesertification threatens the livelihoods of some 1.2 billion people from 110 countries - a number that is likely to increase the population develops.
21 Higher unemployment rate
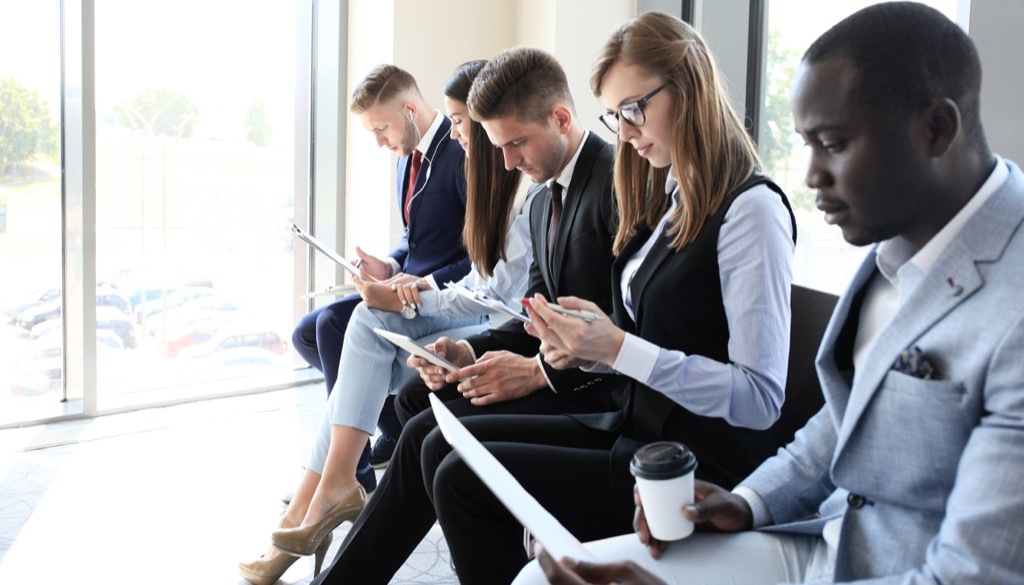

An unsustainable number of people has the potential to drive unless you have opportunities on the workforce. This leads to an article published in theNewsletter Asian Forum Refers to "an imbalance between the supply supply and demand of the latter", which can "[give] an increase in unemployment and underemployment".
22 Decrease in economic growth

With more people out of work, the economy will inevitably take a turn for the worst. The same paper published in theNewsletter Asian Forum Noted that higher unemployment rates have been described in a "low economy and investments ... low economic growth and a low standard of living".
23 Exhausted public funds

"Even among the developed countries, the growth of the growing population would require increased expenditure on basic infrastructure, resulting in an expansion of unproductive capital to the deepening of expensive capital", notes an article published in the newspaper.Ecology and society. In other words, overpopulation would require governments to slide in a thin manner in a way that does not lead to increased production or productivity.
24 Fewer non-retained resources

Non-retaining resources are called such because they can not be easily replaced by natural means. These include things like gas, oil and coal. And while we have access to non-retaining resources now,MPH online Note that our supplies will be at the origin of 35 years, even earlier if the population continues to grow as quickly as it is currently.
25 More war

The overpopulation of the constraint implements resources and opportunities can lead to tensions between nations and voltage communities that can start wars. Examining the conflicts of Angola and Sudan, President of the Population InstituteLawrence Smith Noted That, while overpopulation "is not the exclusive factor [for a lack of stability] ... it is so important that it is probably the key factor". And for the future of the planet, checkHow climate change affect your health now and in the coming years.

Watch a Starbucks client sing his order, go viral and divide internet

