Doctors want you to "be ready" for this side effect of delayed vaccine
The symptom has been identified in individuals up to 11 days after obtaining the vaccine.
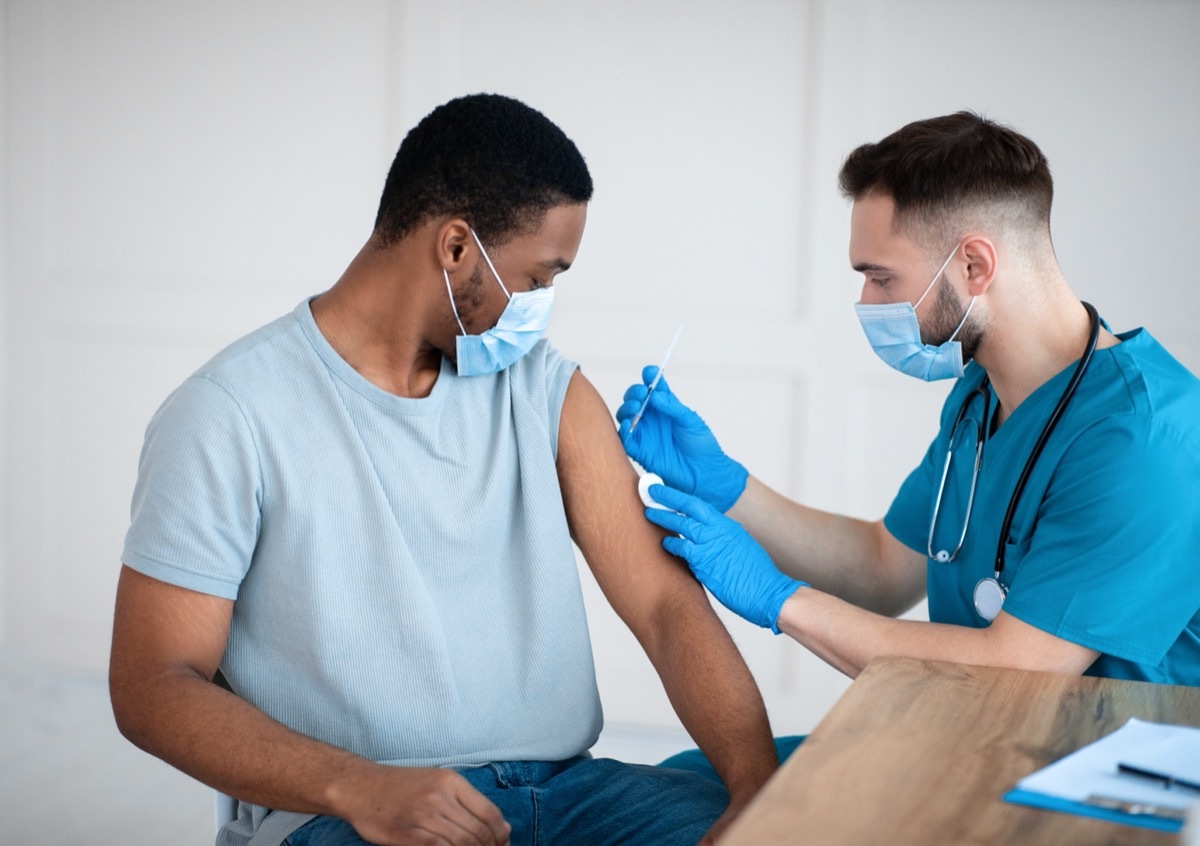
Covid vaccines are being deployed across the United States, much to the pleasure of eligible people to receive them. The vast majority ofThe side effects of Covid vaccines are minimaland similar to those of other plans, including redness and swelling at the injection site, fever, chills, fatigue, muscles and joint pain, nausea andswollen lymph nodes. Most of the symptoms occur in the first days or two of your vaccination, however, researchers say that there is a surprising side effect on Covid vaccine that some people can grow more than a week after getting their shot : a severe skin reaction. Read to read to know how to identify this side effect of delayed vaccine and to find out what this could mean for your second dose. And if you want to make sure that you get the best protection possible, checkDr. Fauci has just said do not take this medicine with Covid vaccine.
The side effect of delayed vaccine has been documented in those who have obtained the Vaccine of Moderna.
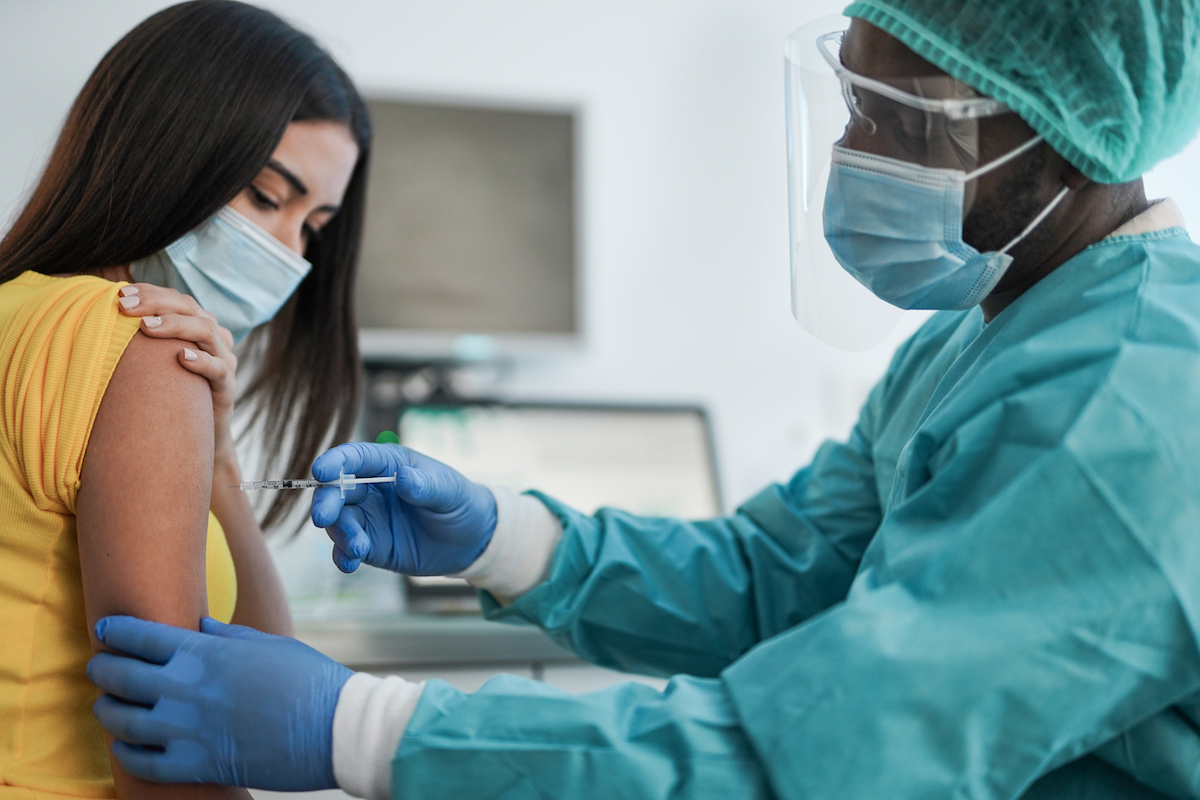

Although dermatological reactions can occur with all the way, not just Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) Covid-Cherchers vaccines have noticed a side effect of delayed Covid vaccine on the skin of some people who have received the Moderna vaccine. In aletter toNew England Journal of Medicine (Nejm), the doctors noted that the reaction may appear on the arm vaccinated as a red, itchy, painful, sometimes elevated area, which covers in some cases a large skin area. And for the latest COVID news delivered directly to your inbox,Sign up for our daily newsletter.
The reaction may appear a significant period of time after your vaccine.
The authors of theNejm Letter explained that, among 12 people who have developed delayed delayed reactions to the Moderna vaccine, the symptoms showed more than 72 hours after the sight of the initially given - the period during which many experts, includingAnthony Fauci, MD, Chief Councilor Covid of the PresidentJoe Biden, saidThe reactions were more likely to occur.
Instead, those with the delayed side effect after the Moderna vaccine experienced the reaction between four and 11 days after administration of their vaccine dose. In most patients, the reaction has erased after about a week. And if you are about to get your shot, know thatThe vaccine against Pfizer can be less effective if you have this common condition.
Even if you have developed the reaction, you should always get your second shot.
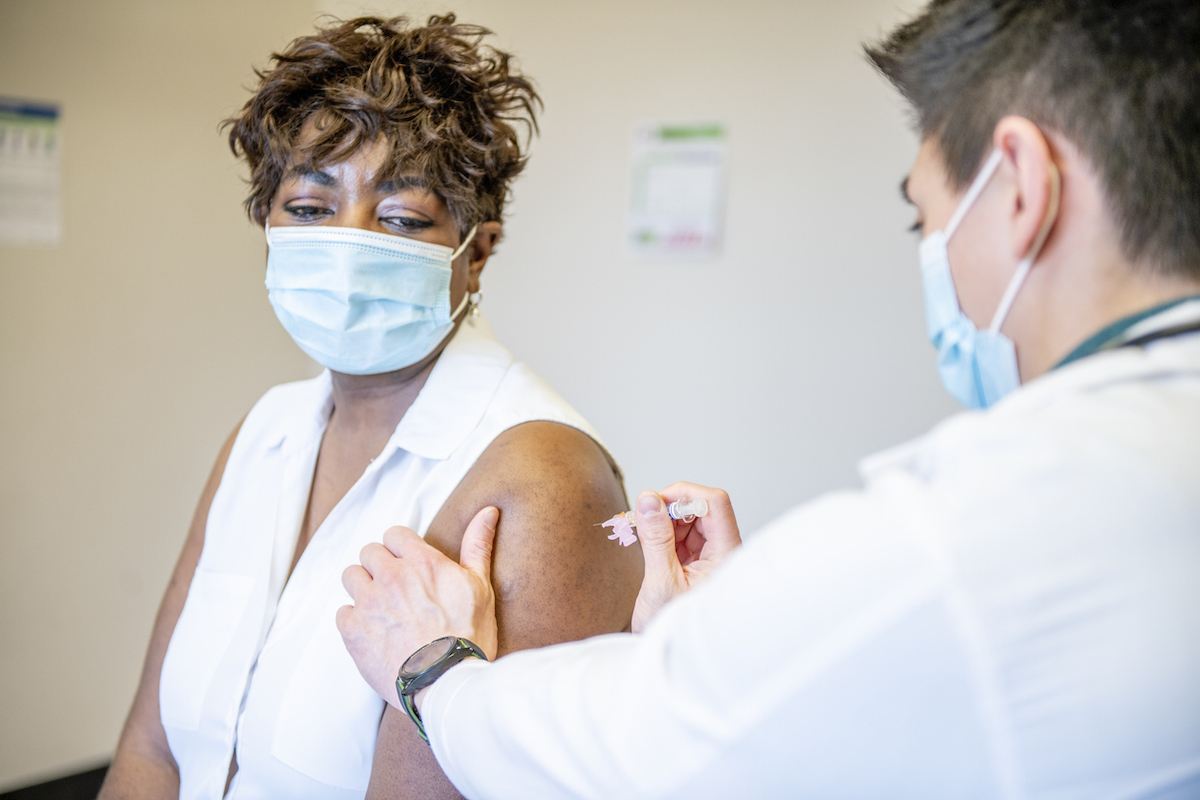
Although the irritation of the delayed appearance skin associated with modern vaccine can be uncomfortable, it should not prevent you from receiving your second dose. If you have the dermatological reaction, it can be a good sign in the long run.Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, Director of the Global Health Dermatology at MGH and Co-author of theNejm letter, note that theThe reaction was probably an indication that the immune system of a person had activated to fight the virus. "Overall, this data is reassuring and should not discourage people from getting the vaccine," Freeman explained in a statement. And for more about what you should not do post-shot, checkDo not do this before a month after your Covid vaccine, experts warn.
But it is possible to get the reaction twice.
According toNejm Authors, half of the people who have developed a reaction after their first dose of vaccine had a reaction after their seconds. However, after the second dose, the reaction occurred faster, usually within 48 hours after receiving the vaccine. And although many have reported that their side effects, including fatigue and fever, were worse after receiving the second cap, delayed skin reaction was not more pronounced after the second dose of the vaccine. And for more than your second dose, checkDoctors warn you of "being prepared" for this after your second dose.
You should not treat the reaction with antibiotics.
While the reaction of documented skin in some people who have received the Moderna vaccine may seem similar to an infection, it should not be treated in the same way. "Delayed skin hypersensitivity could be confused - by clinicians and patients with cutaneous infection"Erica Shenoy, MD, PhD, Associate Manager of the MGH Infection Control Unit, has co-written theNejmLetter, said in a statement. "These types of reactions are however not infectious and therefore should not be treated with antibiotics." The majority of patients who experienced the reaction treated with antihistamines, ice or corticosteroid drugs. And for the latest guidelines on the pandemic, The CDC is about to announce this big CVID guide change. .

Restaurants can always do it when an employee gets coronavirus

The beautiful Photoshoot of Giovana Ewbank with Chissomo girl
