This popular medicine will not really help your back pain, the study says
Although this medicine is approved by clinical guidelines, it does not really work.
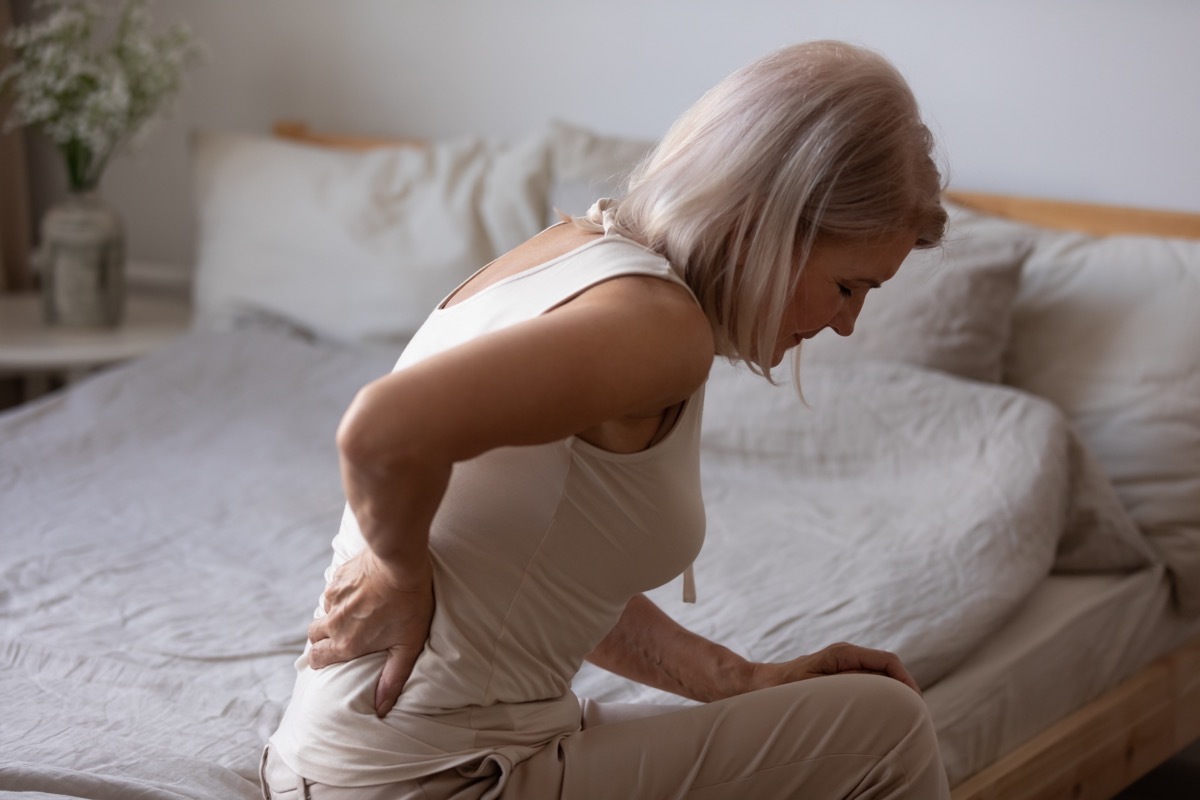

If you are one of the millions of Americans who are experimenting withBack acheYou are probably ready to take pretty much any medicine that promises you a relief. There is a handful of pain reliefers on the market that targets the discomfort of the back, then there are other medicines that doctors sometimes prescribe labels off label to solve back pain. With regard to the last category, some options may be less effective than others. A recent study revealed that a type of medicine that is often prescribed for back pain is not all that is useful. Read it to know which medicine will not relieve your back pain and for more treatments to avoid, discoverThe relief of a pain you should never take for your back, a new study indicates.
Antidepressants are largely ineffective for the relief of back pain.

If you are on antidepressant drugs to lighten your back pain, you may want to reconsider what you are taking. A study by 2021 January from the University of Sydney published inThe BMJ have found that antidepressant drugs, while being widely prescribed for back pain, areinefficient by treating this condition. The study, which has compiled more than 33 previous studies and 5,300 participants, found that the inhibitors of the recapture of serotonin-norepinephrine (SNRIS) reduce only slightly reduced back pain after three months of use.
"The effect was small-A average difference of 5.3 points of the pain balance relative to placebo - and it is unlikely that most patients "by a statement attached to the study. However, researchers have recognized that some patients can choose to try antidepressants for the small chances of reducing pain. And for more medications to pay attention,If you take these 2 over-the-counter medications together, you put your liver at risk.
Antidepressants were slightly more efficient to deal with the pain of osteoarthritis.

The study concluded that antidepressants had a slightly stronger effect on the attenuation of the pain of osteoarthritis, especially in the hip and knee, after three months of use. The average difference was 9.7 points on the scale of pain relative to placebo, which means that "an interesting effect could not be excluded".
Antidepressants are widely prescribed to patients with osteoarthritis. The study noted that "the osteoarthritis guidelines, such as those of research osteoarthritis Society International (OASSI) and the American Rheumatology College recommend from duloxetine for pain management". And for drugs to avoid,If you take this medicine common to sleep, stop now, a new study says.
Antidepressants are widely approved for pain management, but experts do not know why they work.

According to the study, "antidepressants are approved by most (75%) of clinical practice guidelines for lower back pain". But although antidepressants are widely prescribed for pain management, the reason they work in some cases are not perfectly understood. The Mayo clinic assumed that "antidepressants can increase neurotransmitters of the spinal cord thatReduce the signals of pain. "But relief is not immediate and even when it is reached, it is usually moderate.
People with chronic pain often end up developing depression next to their condition. The use of antidepressants is therefore particularly likely to handle both evils, the Mayo clinic noted. And for more useful information delivered directly in your inbox,Sign up for our daily newsletter.
Experts suggest trying non-drugred treatments for back pain.
The researchers in the study finally conclude that drug treatments "are largely ineffective for back pain and osteoarthritis and have the potential for serious injury. We have to work harder to help people with these disorders to live with their Pain without resorting to the prescription buffer. "
The American College of Physicians (ACP) recommends to physiciansAvoid prescribing drugsfor acute backaches. "Non-pharmacological treatment, including superficial heat, massage, acupuncture or handling of the spine, should be used initially for most patients with acute or subacute bass pain because they will improve in the time whatever the treatment ", according to the ACP. And for drugs that could keep you at night, If you can not sleep, this over-the-counter medication could be the reason why the experts say .


