Training errors damaging your body, according to science
Before you put your sneakers instead, check out this list of physical condition security check.

Exercise regularly is one of the best things you can do to ensure a longer life. No joke, right? You have heard a zillion times. And the Council is supported by tons of scientific data. For example, a meta-analysis of the studies examined in theJournal of Landering Research has shown that mortality for all causes is decreased by 35% of people physically active compared to inactive persons. Exercise SFSTE every risk factor for major mortality through the board: hypertension, type 2 diabetes, obesity, coronary heart disease, stroke and cancer.
So, there is little evidence that exercise exercise will make you. Sorry, you can not use self-preservation as a reason to blow your workout.
But there are some bad training habits that can have harmful effects on your body. Here are some exercise errors that can harm your body in one way or another. When you have corrected them correctly, optimize your SROW SESH sweatshirt with the14 best foods for better training results, according to experts.
Starting a workout without having a cardio balance first.
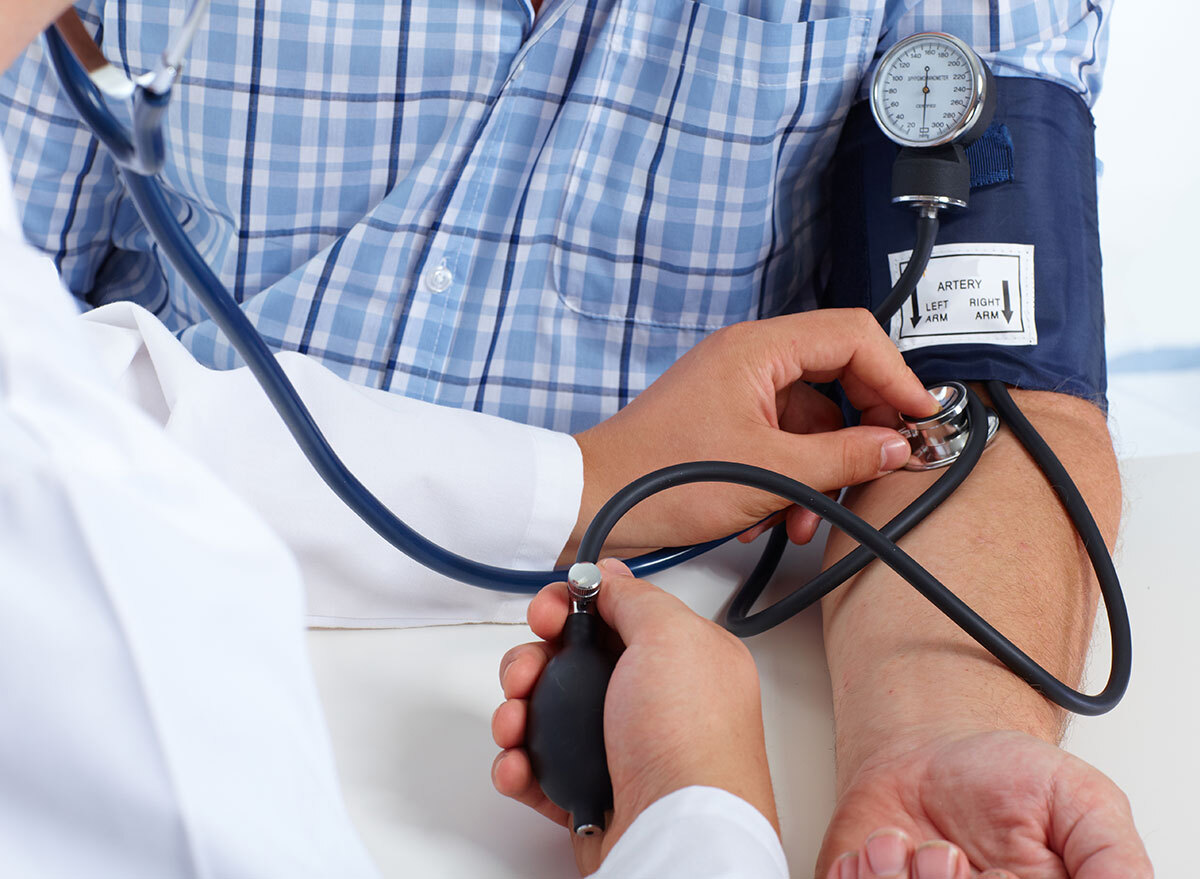
You have heard the Standard Doctor Board for years: Get a balance sheet before starting an exercise program. Most people do not do it, and it's a misstep that could finish shortening their lives. Here's why: There is a slight risk of heart attack or heart complications when you start an exercise program, especially when fitness at ground level. But let's say you exercise regularly without problem. If you have high blood pressure and do not know how your cardiovascular system responds to the exercise, you could prepare for problems, suggests a study appearing in theJournal of the American Heart Association.
Using data from a long-term American study called the Framingham Heart Study conducted by the national heart, lung and blood institute, researchers analyzed the blood pressures of participants during and following a "sub-layer exercise" ", That is, an exercise slightly below the person. effort. The analysis showed that the high systolic blood pressure during exercise and recovery was associated with two measurements of risk thickness of cardiovascular diseases of the mucosa of the carotid artery and the thickness of the cardiac muscle on the left side. On the positive side: the data revealed that people who had a good recovery of systolic blood pressure after exercise benefit from a protective effect of training, a reduced risk of 17% cardiovascular disease.
"How our blood pressure changes during and after the exercise provides important information about whether we will develop the disease in the future," wrote the study authorDr. Vanessa Zanthakis, an investigator for the Cardiac study of Framingham. So, exercise without knowing if you have hypertension, silent murderer, could eventually shorten your life. Related:The easiest way to reduce your blood pressure.
RELATED: Sign up for our newsletter for daily recipes and new foods in your inbox!
Too intense weight weight.

By pushing too hard into intense and repetitive exercises as a bodybuilding, or suddenly increase the intensity of exercise when you are out of shape, can lead to a rare, but serious and damaged muscular disease called Rhabdomyolysis, according to theAmerican Academy of Medician Assistant Journal. Also known as Rhabdo, the condition causes the rupture and rupture of muscle cells and proteins in the blood, causing such symptoms such as extreme muscle pain and a dark urine. Serious cases can result in acute renal failure, cardiac dysrythmia and even death. It can happen in trained athletes as well as people out of shape that start an intense workout too quickly. Repetitive eccentric weight lifting (that is, exercises that highlight the muscular enlargement of an elevator), hyperthermia and dehydration contribute to the risk of Rhabdo, according to a review ofSports health.
Exercise by pain.

"No pain, no gain", is a notion of obsolete muscle head and a myth that has been perpetuated in gymnasiums throughout the country. While muscle fatigue is the key to growth and strength, pushing yourself through the pain is a mistake. "Pain represents an injury", doctor of sport medicineDominic King, do told Cleveland Clinic Health Essentials in ablog. This can be the result of overuse or too much stress placed on a muscle or tendon. "People use to say that you have to" suck it "or simply push the pain. But the pain is your body trying to tell you something and you have to listen, "says Dr. King.
Get your "Asana" kicking to power yoga.

High chronic stress is associated with increased risk for everything, psychological disorders such as depression and low self-esteem to physiological diseases such as coronary artery disease and diabetes. It's not a wonder while more than more27 million Americans have adopted yoga practice, a popular stress management strategy. But it's if you do Hatha, the style of meditative yoga, and not necessarily, if you practice the Vinyasa style or the Power Yoga, according to a study 2020 in theInternational Journal for Environmental Research and Public Health.
Researchers in the Kinesiology Department of the Samford University of Alabama have recruited physically active women who did not practice yoga for the study and put them through a single 30-minute session of Hatha Yoga and Vinyasa Yoga separated from 48 hours. Each time, participants received an autodérée anxiety questionnaire to complete and the front and after-session saliva tests for measuring the levels of hormonal stress cortisol. The results showed a significant reduction in cortisol levels and anxiety after meditative style yoga, but not after electric yoga. For more ways to reduce cortisol levels, check these21 best foods when you are stressed, according to dietitians.
Exercise in extreme heat.

Every summer, you hear some stories of high school students or university football players who are dying of heat strokes or the fight against extreme heat. But this only happens athletes and this does not happen only in summer. More than 600 people in the United States die from extreme heat-related incidents each year, depending on disease control and prevention centers (CDC). It is known to occur even inside the winter deaths in saunas and hot yoga classes. "Exteller heat (EHS) can affect apparently healthy athletes, even when the environment is relatively cool," says aposition Thermal disease by the American College of Sports Medicine. Thermal disease and its most dangerous forms, heat depletion and heat tray, result when the body is unable to cool and overheat. The symptoms include intense perspiration or not sweat when nausea, a breathtaking crisis, nausea, high temperature and confusion among others.
For more advice on economics of life, checkEvery day, you damage your lungs, according to doctors.

Here's why you should think twice before rolling an elevator right now

This ingredient in more than 1,250 foods may not be sure, a new study says
