Make a change to your diet could "reprogram" your metabolism, a new study says
No, they are not carbohydrates. This could be one of the biggest advances in plan for decades.

More than two decades of western wisdom have advised us with a basic rule: if you wantlosing weight, just cut yourcraband increasesprotein. However, a new revolutionary study by a team of metabolism researchers and endocrinology has led to the discovery of another aspect of food that, as scientists say, "had the most powerful effect" to accelerate The metabolism ... and, as they suggest, a change in the foods you eat could even help you live longer.
Dr. Dudley Lamming is a faculty member of the Department of Medicine at the University of Wisconsin-Madison in the division of endocrinology, diabetes and metabolism. His latest studiesPress release stipulates that in 2014, the width accomplishes an Australian study that had come on something remarkable: the mice that had been nourishedless The amount of protein was the healthiest.
RELATED:15 underestimated weight loss tips that actually work
This went against what our culture preached on nutrition and well-being, but the drop was aware that there was more science behind the effect of low protein. Since then, he and graduated students from his laboratory "have discovered a little known but robust model of both models and animal humans", according to their new study publication, that is, " The schemes are high in the three amino acids at the branched chain, BCAAs, are associated with diabetes, obesity and other metabolic diseases. "The three BCAAS are leucine, isoleucine and valine, all this That humans can not do alone and must therefore get by consuming them in the food we eat.
Therefore, the coward and his team believed, reducing leucine, isleseucine and valine "can counter these metabolic ailments and even prolong the healthy life of rodents."
Read it to see what happened when the researchers adjusted the proteins mice in their eating laboratory - and do not missSecret exercise tips for a better body after 40 years, say experts.
The researchers administered a Western regime.

They went ahead to test their hypothesis, nourishing mice with a high fat, high in sugar, classicWestern for a few months.
The limitation of the isoleucine had a major effect.

Once the mice became obese, lambineae and his team switched mouse regimes. They recognized that, by limiting the Isoleucine of amino acids to the branch chain, "the mice started eating more food but nevertheless lost weight." Why? They indicate: "Weight loss was mainly caused by a faster metabolism, where the body burns more calories than heat while resting."
In addition, they found that "mouse regimes fed at low isoleucine were wider and demonstrated sugar metabolism in healthier blood."
RELATED:The surprising effect reducing sodium can have on your blood glucose, a new study indicates
What only this discovery could mean for us ...
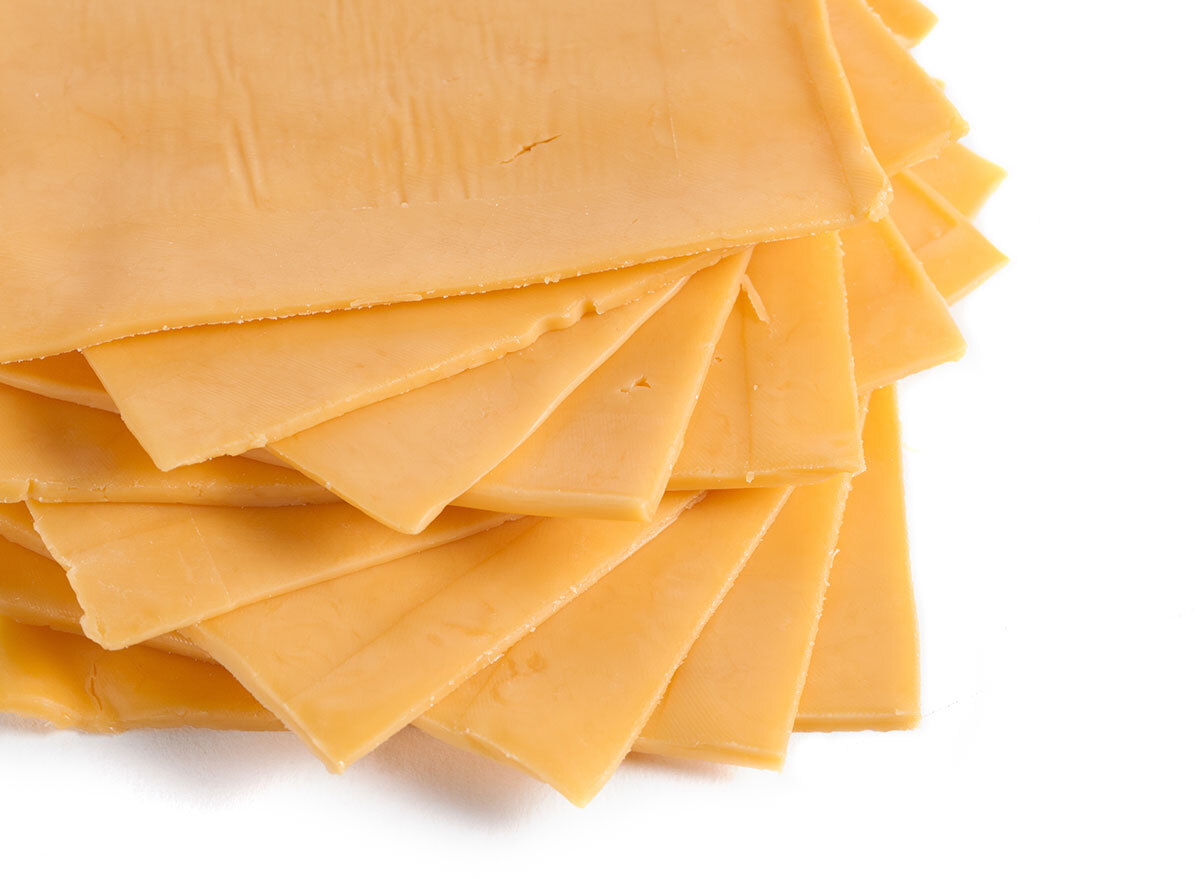

Since then, according toMedical News Today, Isoleucin is abundant in foods like meat, poultry, fish, eggs, cheese, lentils, nuts and seeds - most of them who are encouraged in low-grade plans in carbohydrates such as Keto (likeKourtney Kardashian follows) Or paleo-limiting our consumption of these could prove to help us lose weight. In addition, it is not only because of the high fat content in some of these foods, but because of the presence of isoleucin.
The restriction of the valine has also shown an effect.
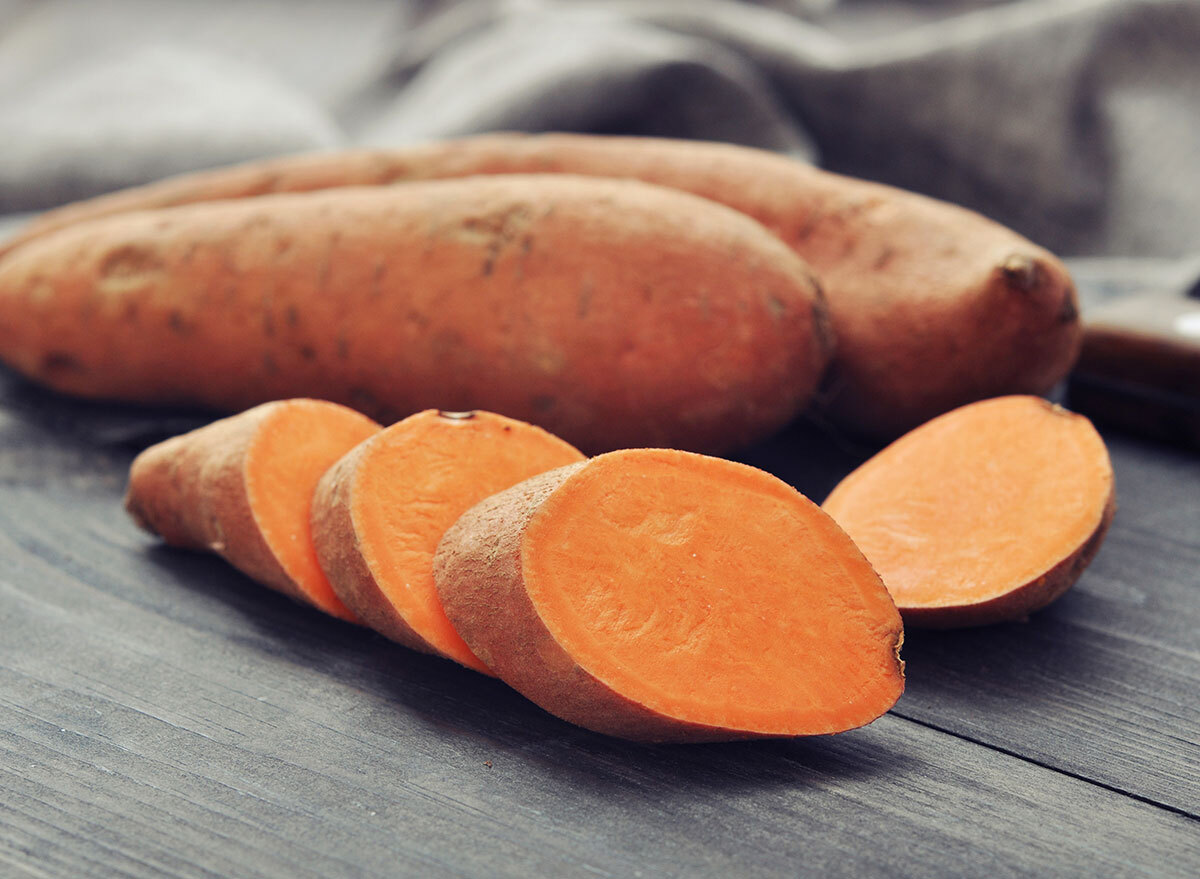

Meanwhile, "Valine Restricted Diets had similar but lower effects" to the restriction of isleucina. Valine is found in foods like soft potatoes, asparagus, spinach, peas, mushrooms and peanuts.
RELATED:This food becomes a more important allergy threat than nuts, says the data
Limiting leucine affected metabolism differently.
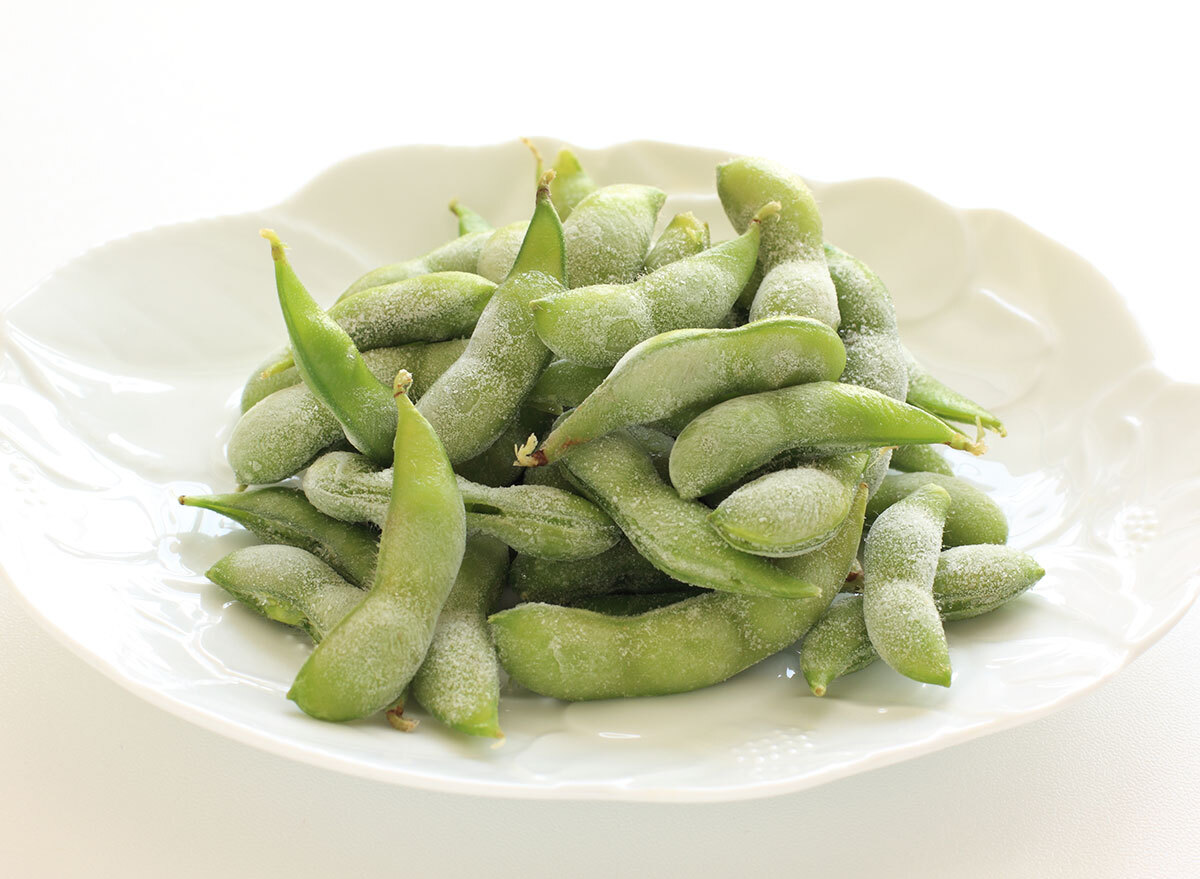

Finally, the researchers stated that the reduction of leucine levels "had no advantage and may even be detrimental to" metabolism. High leucine food includes dairy, soy, beans and legumes.
With more scientific research, this could change the way we think we are planning a diet.
Lamming says that this discovery provides an opportunity to rethink the regimes because "proof of animal models suggests that low protein regimes help lose fat, even with normal caloric consumption by reprogramming the metabolism", according to the release of the metabolism ", according to the release of the 'study.
RELATED:A major effect of drinking milk, a new study says
The researchers emphasized another important discovery.

Interestingly, it is more and more deeply revealing that these amino acids also affect men and women differently, due perhaps to our hormonal reaction. One of the graduate students of the department, Nicole Richardson, also tested a diet in mice that contained only a third of the normal amount of BCAAS. It was not a restricted calorie system; Animals could eat as much as they wanted. "
The discovery of Richardson's experience was that "male mice that ate the diet of their lives lived about 30% on average - about eight months more months" than female mice. Lamming and his team suggest that, because a lot of endocrinological and metabolic research has been conducted on male mice, it may be time to consider how the effects of diet, protein and amino acids vary according to gender . (An example - check-outA major side effect of being overweight for men, a new study says.)
Sign up for theEat this, not that! newsletter For nutrition, you can use and continue reading: