Do this the night Slashe your risk of Alzheimer, a new study discovers
A habit was noted to help keep the brain healthy over time.
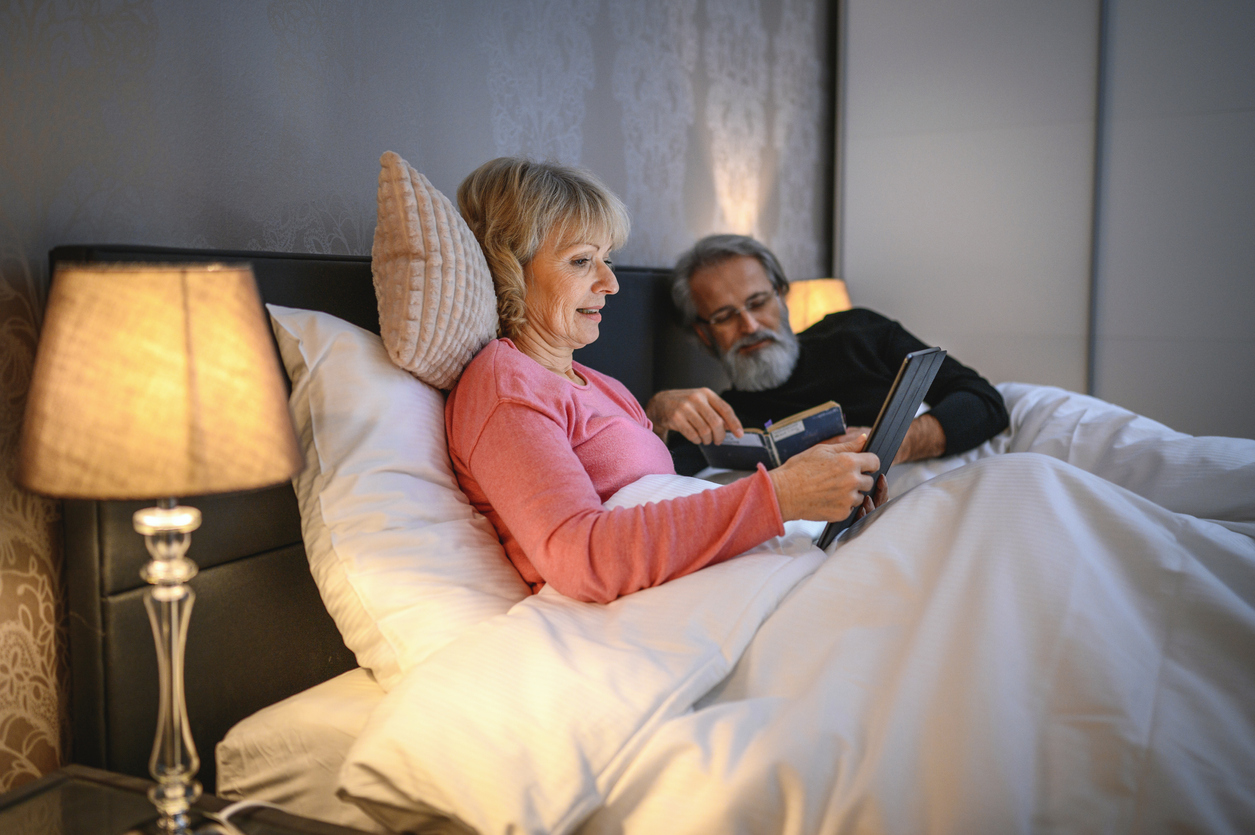

When it comes to keeping an eye on our health, things like our daily diet and our exercise routine generally come to mind. But even in the evening,some surprising habits can play an important role in the rigor of serious evils. And according to a new study, making sure to do one thing each night could significantly reduce your risk of developing Alzheimer's disease. Read it to know what to give priority as part of your nocturnal ritual.
RELATED:If you notice this in the bathroom, it could be an early sign of dementia.
Getting enough sleep Every night can help reduce your risk of Alzheimer's disease.

In a study published February 10 in the scientific newspaperPlos genetics, scientists have found thatSleep enough every night Actively reduces the probability of developing Alzheimer's disease later in life. According to their research, the reason for health stimulation has just maintainedHealthy sleep habits and avoid sleep interruptions, allowing the brain to get rid of the amyloid-beta protein 42 (AB42) before being able to form tufts in the brain. These clusters of proteins are generally considered a precursor or a warning sign of the appearance of Alzheimer's disease.
"The circadian regulation of immune cells plays a role in the complex relationship between the circadian clock and Alzheimer's disease", "Jennifer Hurley, PhD, the primary author of the study, an expert in circadian rhythms and associate professor of biological sciences in Annésaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI), said in a declaration. "This tells us a healthy sleep model might be important to mitigate some of the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease, and this beneficial effect could be transmitted by an immune cell type called macrophages / microglia."
The circadian rhythms define different body functions moving that keep you healthy in many ways.

The study relies on previous understandings of the importance of circadian rhythm in overall health. According to researchers, the circadian system uses a core set of "clock proteins" that helpsRegulate body functions This takes place during the day or night by controlling hormone and enzyme levels in the body. This allows your body to be prepared for different tasks, whether you are asleep or awake.
The natural cycle allows the body to enter a "rhythm" that controls all immune responses specific to body temperature during the day and all night. However, when the cycle is interrupted by not sleeping enough sleep or is constantly awakening at night by health problems such as sleep apnea, it increases the risk of serious health problems such as diabetes, cancer. Cancer and Alzheimer's disease.
RELATED:For more information up to date, sign up for our daily newsletter.
Get enough sleep helps your body cleave the brain of harmful proteins related to Alzheimer's disease.
According to team research, immune cells called macrophages, which operate to rid the body of the undesirable material, contribute to clarifying the harmful ab42 of the brain during a process called phagocytosis. The previous studies carried out by Hurley and his team found that the levels of RNA and macropham protein went up and fall with the circadian rhythm of the body. The new study established that these oscillations of certain enzymes helped produce two components of the cellular macrophage structure called heparane sulphate proteoglycan and chondroitin sulphate proteoglycane. More specifically, the lower levels of the two proteoglycans facilitate the task of macrophages to clean the brain of AB42.AE0FCC31AE342FD3A1346EBB1F342FCB
The last experiment has tested the changes made by the circadian rhythm and how they are related to cell surface structures, discovering that the amount of AB42 that healthy macrophages can clarify the same sleep cycle plays an optimization factor. process. In comparison, other immune cells are not regulated by the internal clock of the body not sharing this model.
"What is clear is that it is quite timed by the circadian clock," explains Hurley. "When there are many of these cellular surface proteoglycans, macrophages do not fit the AB42. We are not sure why it would be, but there is definitely a relationship. In theory, if we could stimulate this pace We may have increased the game of AB42 and accredit the brain, "she concludes.
Further studies have found that the night of six hours or less each night could increase your risk of dementia.

While getting enough sleep overall is essential, another study published in April 2021 in the scientific journalNature Communications found thatSleep six hours per night or lessOne night was linked to aIncreased risk of dementia in people aged 50 to 60 years. Researchers at the INSERM French Health Research Institute analyzed data from a long-term study of the University College London, who followed 7,959 British between 1985 and 2016. The team then compared the health of Adults who do not have enough sleep to people who slept the seven hours recommended.
Overall, 521 participants developed dementia throughout the study and were diagnosed at an average age of 77 years. The results revealed that the participants who slept seven hours per night had the least case of dementia. In comparison, there were 30%Increased risk of dementiaIn those who have consistently focused on a night of up to six hours a night of 50 and 60 years old.
"Many of us have had a bad night's sleep and probably know that this can have an impact on our memory and the short-term thought, but an intriguing question is whether long-term sleep patterns can affect our risk of dementia ",Sara Imarisio, PhD, Alzheimer's Research Research Manager U.K., said in a statement in response to the new study. "We know that theDiseases that cause dementiaStart up two decades before the symptoms such as memory loss began to show, mid-life is therefore a crucial period for risk factor research. "
RELATED:98% of people with Alzheimer first develop this symptom of this symptom..


