How climate change affect your health now and in the coming years
The growing temperatures are bad for the planet, but they also have serious effects for people.

We have heard about rising oceans and destroyed vegetation due to rising global temperatures for decades. And while warnings have more than eager and urgent, we often neglect that climate changeaffects health not just the earth, but also those who live it.
If you thought that climate change did not blow humans into the here and now, consider that some parts of the world (likeAustralia andScandinaviaand even from the United States inTexas) Continue to see record heat waves, as well asHeat-related diseases, who can be fatal. In Australia, for example, the number ofHeat-related deaths From 2000 to 2009 amounted to 532 years, almost as numerous as the experienced country in the three previous decades combined.
EEnvironmental hazards directly affect our ability to live, breathe and thrive in the present and continue to do so. Read on how climate change is currently affecting our health and how it will affect our health in the future.
Now: we have trouble breathing.

Climate change leads to changes in air quality, both pollutants and mancommentsnatural allergens, like pollen. And people with respiratory problemsAre particularly sensitive to changes in quality and temperature of the air, which already becomes a problem.
A 2018 study published in theAmerican Journal of Respiratory Care Medicine and Critics found that air pollution has already resulted in more visits for people with these respiratory problems across the United States.
With an increase of 20 pieces per billion (ppb) of ozone, the rate of visits to respiratory problems increased by 1.7% in children, or 5.1% in adults under 65 and 3 , 3% in adults over 65 years old.
Now: the disease spreads more widely.

Increased hot and wet conditions - that climate change has created more mosquitoes, creatures that are notorious to spread diseases such as Western Nile virus and Lyme disease. These are calledVector transmitted diseases (VBD)And vectors may include fleas, ticks, lice and rodents, in addition to mosquitoes.
When a disease is mainly widespread by an animal or an insect, it is generally limited to a geographical area where this animal or insect can live. But when temperatures rise, the populations of some animals and insects are therefore. Mosquitoes can now live at higher altitudes that have traditionally been malaria, because insects could not survive there. A 2014 study published in the journalScience I reviewed cases of malaria in the Antioquia region of Western Columbia from 1990 to 2005 and the Zeyit Zone of Central Ethiopia from 1993 to 2005. Researchers have seen a correlation between malaria epidemics and rising Temperatures in these malarialess environments.
Now: our contaminated water makes us sick.

Hurricanes and rising temperatures go from hand. NewspaperHealth affairs"The devastation caused by Hurricane Harvey was part of the result of the temperatures of the Gulf's surface for the first time on a record never falling below 23 ° C." Over the last two or three decades, the United States has seen an increase of 45 to 87% of the frequency of hurricanes in Class 4 and 5 as a result of climate change, according to a 2012 study published in theClimate log.
These storms in turn affect the quality of drinking water and therefore damage our health.Flood and runoffCan contaminate water with bacteria, viruses and parasites, which lead to diarrheal diseases that cause dehydration. And without clean water to rehydrate, the problem becomes worse. For example, a significant 2008 study published in the journalEmerging infection diseases Found only after the Hurricane Katrina, the number of cases reported from Western Nile has increased sharply in the regions affected by the Hurricane of Louisiana and Mississippi.
Contaminated water can also grow toxic algae flowers that can make people even sicker. And if it was not serious enough, the amount of water of a flood can cause overflow and a mixture of drinking water.
Now: We are more at risk of skin cancer.
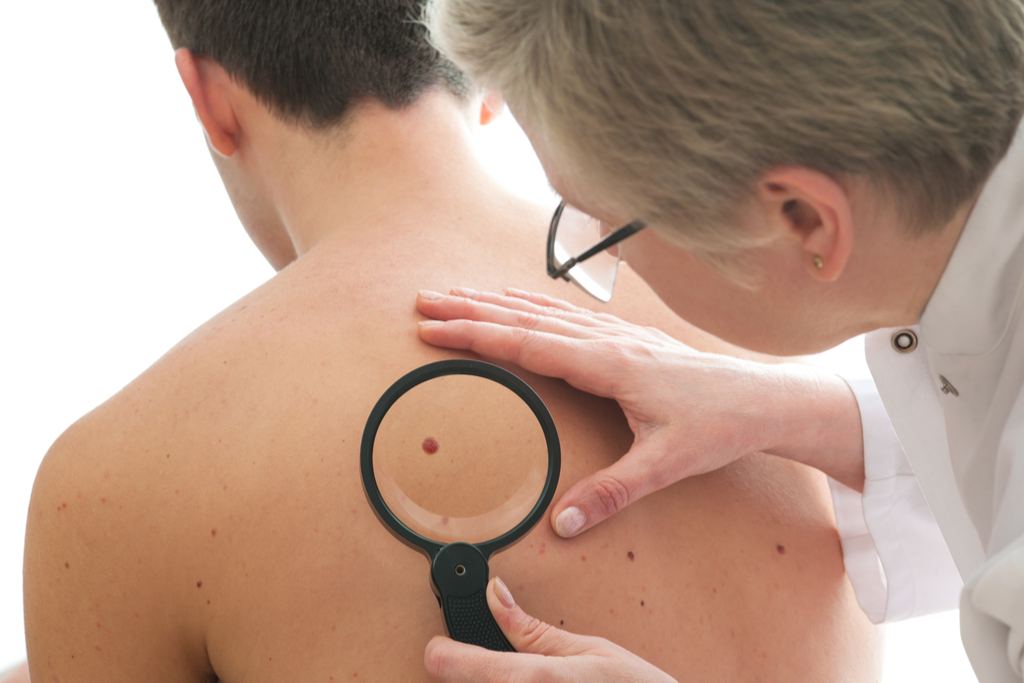
Climate change and exhaustion of ozone are two distinct-but linked problems. The growing level of carbon dioxide and CFC gas (chlorofluorocarbons)In the atmosphere has both a fueled climate change and resulted in the depletion of the ozone layer, according to a 2012 Harvard study published in the journal.Science. Climate change also damages the layer of the atmosphere that protects humans fromDamage UV rays. And when the UV rays are going through, ourRisk of skin cancer increases considerably.
A notable 2009 study published in theJournal of the Royal Society of Medicine watched the connection between climate change andskin cancer. The researchers noted that "the depletion of ozone resulted in an increase in skin cancers and disturbingly." And a 2002 study ofT-cited published in the magazineThe lancet found that an increase in skin cancer cases in Chile in people under 50 - from 12% to 20% of the population - was directly related to the depletion of the ozone layer.
Now: our allergies are worse and durable.

Of course, compared to skin cancer, allergies may seem less worrying but more and more people areallergy Every year and each climate change seems to be the culprit.
2005 pivotingHarvard The study revealed that rising temperatures and increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causes plants to be flourished earlier in the year (Kickstarggy Allergy Season) and encourages them to produce more pollen and mushrooms supplements that they had in recent decades. APaper 2014published in theReview of European Respiratory Channels explained thatEnvironmental conditions such as extreme heat, high humidity and cyclones are consequences of climate change - have been associated with an increase in allergies.
In the future: our air and our food will be contaminated with mercury.

The Arctic Ocean is loaded with Mercury, hidden under the permafrost where it has been trapped since the age of ice. Usually, the element only binds by living matter. But because of the low temperatures of the Arctic, the plants are not fully decomposed, which means that their roots are frozen and still containtoxic mercury. The substance is extremely toxic, causing visual and verbal impairment, weakness, poor coordination and all kinds of other health problems in humans who come into contact with even small quantities.
The bad news is, according to a 2018 study in the newspaperGeophysical search letters,About 32 million gallons of mercury have accumulated in the Arctic, about to be released if, or more likely when, the permafrost thaws.It is the equivalent of 50 Olympic pools - "twice as much mercury than the rest of all the soils, the combined atmosphere and ocean", as the authors of the study put it - it could be released in the Arctic and from there, in the atmosphere.
And this empires: Mercury continues to build when it moves through the food chain (process called biomagnification). It is difficult to say how much it would damage the release of the release of these 32 million gallons, but it will probably have reached the wetlands and the Arctic aquatic ecosystems, then soon contaminate food supply. humans from there.
In the future: we will suffer more cardiac crises.

Heart disease Is already the leading cause of death in the United States and climate change is going to make it more deadly.Increasing temperatures are not just bad for your lungs - they arebad for your heart, too much.
2011published studyin theAmerican newspaper of epidemiologyfound that the increase in temperature levels can be bad for the heart of a person. According to the study, high temperatures in the summer months in the United States were associated with a decrease in the regularity of the heartbeat of the subjects. And a drop in cardiac variability is linked to an increased risk of death after aheart attack.
And then, of course, there is the question of atmospheric pollution, whichincreasesFollowing climate change, according to theCenters for Disaster Control and Prevention (CDC). Pollution has also been associated with increased risk of cardiac crises. In fact, a 2013meta-analysisPublished in the newspaperThe lancetfound that air pollution increases the risk of suffering from a heart attack of 4.8%. This more important risk is partly because pollutants encourage inflammation of the lungs, which causes inflammation of the heart.
In the future: we will not receive enough nutrients.

One of the biggest dangers presented by climate change is the damage it should do to our food supply due to drought, soil erosion and greenhouse emissions.
A 2010 study published in theInternational Life Cycle Evaluation JournalI found that more than a third of the land of the planet risk desertification, which means that a serious drought could be the difference between the soil and the cultivated lands that is too degraded to grow. For example,National Geographicstresses that most of the cultures of Egypt are grown in the Nile Delta, but the intrusion of erosion and seawater that would result from a drought may leave the whole region withArable.
Another 2018 study published in theActs of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America Discovered that if greenhouse gas emissions are continuing on their current trajectory, the world's production of vegetables and legumes could decrease by 35%, for lack of water and increased salinity. In fact, according to the study, an increase in the temperature of 4 degrees would result in a probability of 86% that the 4 major corn producing countries of the planet would suffer simultaneous production losses of more than 10% per year.
It's aA huge part of the globe that could be without a sustainable food source, considering that maize is also the main source of nutrition for cows. Malnutrition is a problem in itself, but it also increases the susceptibility of a person to the disease. And talking about that, dSpread rough mold that produces aflatoxin, which is supposed to contribute to the development of liver disease in people who eat contaminated crops, according to a significant study of 2008 in theIntegrative biology log of the plant.
And if everything was not serious enough, one of the climate changea lot of documented effects Tobeen an increase inpests, such as aphids and locusts, according to theNational Institute of Environmental Health Sciences.
In the future: the summers will be laundered hot.

One of the most obvious results of global warming is that hot months will become unbearable. For some, it might seem like the small disadvantage of treating sweat stains and indoor barbecues of the fourth of July. But for many, it could mean a life or death situation.Search published in the newspaperCheekIn 2018predicted that the United States could see minimum summer temperatures could increase by 3.3 ° C. Through the forecasts of the researchers, it means that in the middle of the 21st century, 11,500 Americans could die each year as a result of 'Exposure to heat.
This may be even worse in urban areas. According to the 2014 research of theNatural Resources Advice, the said "Effect of Urban Heat Island "will result in an average increase in summer temperatures of about 1 ° CFollowing On average, compared to rural counties.
In the future: we will not sleep enough sleep.

Climate change is likely to make people's sleep more difficult. It is not only due to the concerns of extreme weather events or all other health risks described here so far. In a document of 2017 published by the newspaperAdvance of scienceThe researchers predicted that if the temperatures continue to increase at the rates they have been, by 2050, we can expect an additional sum of six nights of insomnia every month - and fourteen (nearly half of the month) by 2099.
This is because the internal temperature drop that occurs when you sleep at night is a prerequisite for sleep. In fact, insomniacs often find that a lower ambient temperature helpsfall asleep and stay asleep. As a global temperature increases, we can expect insomnia anda lot of repercussions of this one, including fatigue, anxiety, forgetting and decreasing the immune system response - not to increase.

"Harry Potter" Star Katie Leung said she was said to deny racist intimidation

