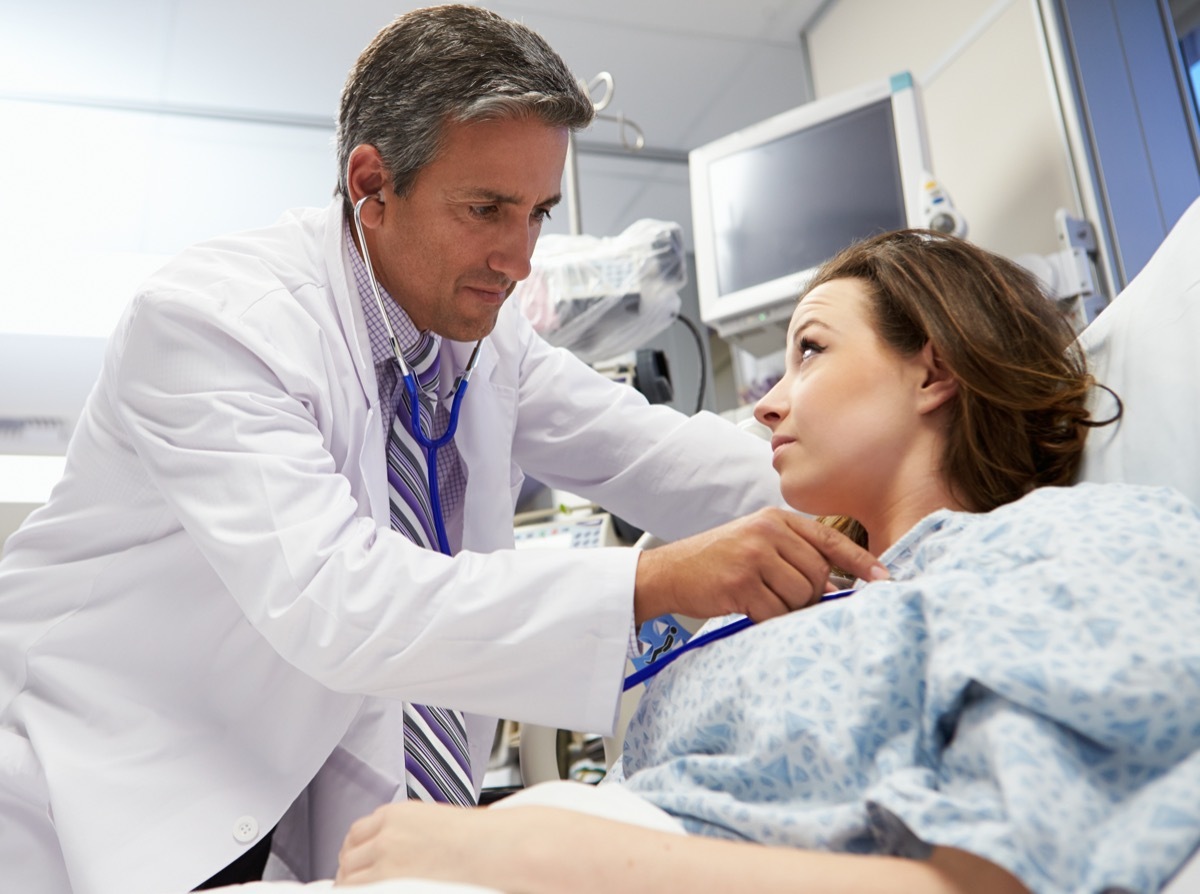
The most recent COVID strain could "weaken" the vaccine, expert warns
The South African covidant mutation can really reduce the efficiency of the vaccine.
Covid continued to change and mutate throughout his life - for the most part, very slowly, creating minimal changes to the virus. However, two new strains of COVID show more significant changes, which have concerned experts. A strain appeared in the U.K. towards the end of December and while this strain doeseager, scientists are safe enough that our current vaccines will bework against. However, the experts are less confident of the efficiency of the vaccine when another new Covid strain has recently appeared in South Africa. Read it to learn why experts are concerned and for more coronavirus crowns,Dr. Faisci just said these 5 very scary words on Covid-19.
The new South African strain could "weaken the impact" of the vaccine.
ProfessorShabir Madhi, which led the tests for the Oxford-Astrazeneca vaccine in South Africa, told the BBC that it is a "reasonable concern" that "the South African variant could bemore resistant"The vaccine. Madhi added that, although it is" unlikely "that the mutation would make current completely useful vaccines, it could" weaken the impact ".
As indicated by CNBC, U.K. Secretary of HealthMatt Hancock said to the BBCToday program it is "incredibly worried About the South African variant. "Hancock said it's" a very very important problem ... it's even more problematic than the new variant of the U.K. "And for more information up to date,Sign up for our daily newsletter.
The mutations of the constraint could make it more resistant to the vaccine.
"The mutations associated with the South African form are really prettysubstantial changes In the structure of the protein "Sir John Bell, who led the development of Astrazeneca-University of Oxford Covid-19 Vaccinal, told the radio. These significant structural alterations could prevent the vaccine from working properly against the new strain.
"The protein has a domain, which binds to human cells - it's called the receiver binding domain, and that is where the virus is fixed," said Bell. "If you get an immune response that protects you, one of the ways to protect you in the path of this link event. So you count on antibodies to bind to this area to prevent the virus from Link to you. It's basically the entire vaccine base. If you get an infection, you do antibodies to this domain that prevents you from reinfecting it. So if you log out with that, you have problems. "
In other words, the last strain can be more suitable for linking and, in a way, antibodies are less effective in prevention. And for more information on the vaccine, discoverThe unique effect of Dr. Fauci is worried with his next shot of Covid.
The vaccine can be adjusted to adapt to new mutations.
Even if the vaccine does not work against the most recent tension, experts believe that the vaccine could be adjusted to reflect the new development of virus proteins. Vaccine expertHelen Rees Told the BBC ", the additional changes in the vaccine should be necessary to resolve new variants, some of the ongoing vaccination technologies could allow it to be relatively quickly." And for more information on the current state of the pandemic,That's how the COVID epidemic is in your state.
We should know if the vaccine works against the new VIPID tension in a few weeks.

Madhi told the BBC that we will know about the efficiency of the vaccine against the new COVID strain "in the coming weeks." Scientists will have to do in-depth tests to understand how the South African strain interacts with the vaccine. And for more information on vaccine distribution,These states had the deployment of the slowest vaccine.

These 21 states need to lock now, declares the report