You have to do this right before getting an influenza shot, let's say experts
This one thing can make all the difference in the effectiveness of the influenza vaccine.
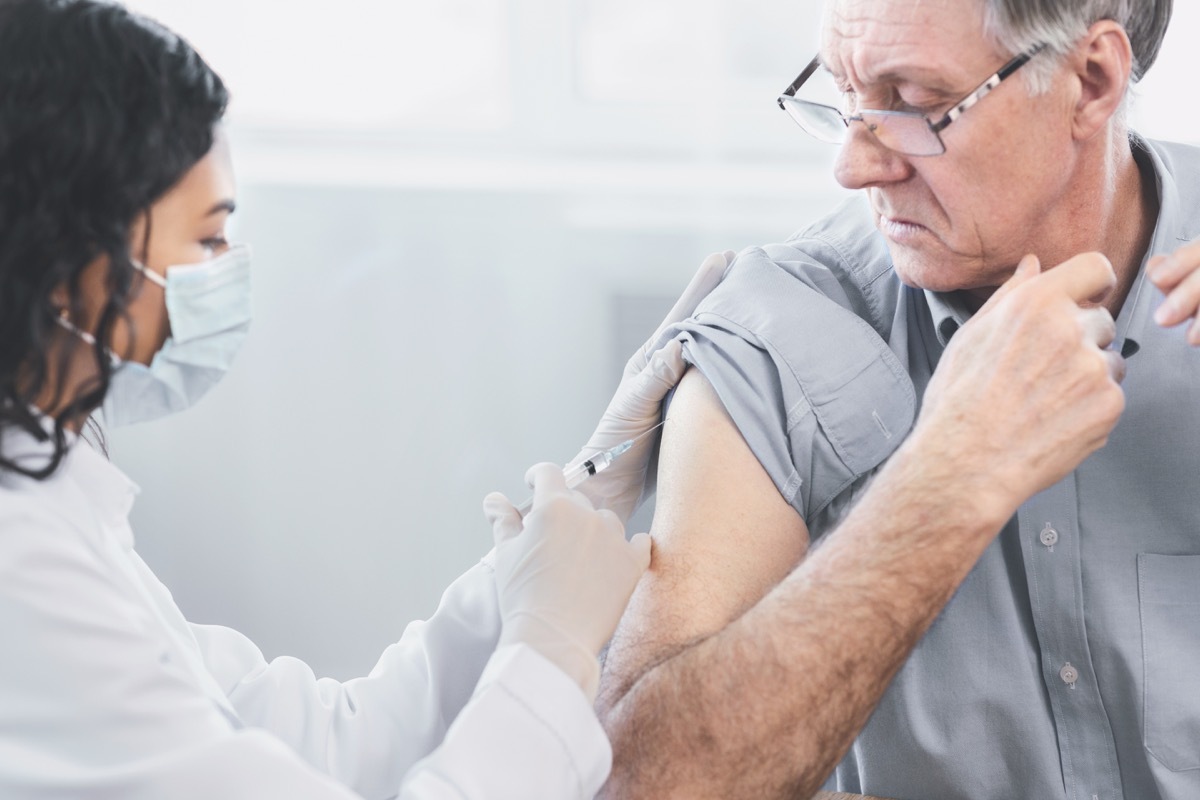
Health experts sayGet a shot this year is more important than ever. With theCoronavirus pandemic still running crawler, Any chance of diverting another disease with an easily available vaccine is better than nothing at all. Of course, aThe shot of the flu is not infallibleAnd you could always get the flu-but there may be a way to stimulate his power of protection. According to experts, you must make sure you have a good sleep just before getting an influenza shot to increase its effectiveness. Read it to know how sleep can help your influenza shot work better, and for more influenza, find out if you wereBorn in the decade that makes your risk of soar influenza.
Bad sleep the week before getting an influenza shot can possibly rendered ineffective,Matthew Walker, Doctorate, a neuroscientist and the best author ofWhy we sleep, says CNN. This is because insufficient sleep can lead to the production of less than 50% of the normal antibody response, he explained.
According to Walker, two major studies speak at this point. A noticeable 2002 study published in theAMERICAN MEDICAL ASSOCIATION JOURNALfound aClear decrease in the response to the influenza vaccine For those who had reduced sleep for four days before being vaccinated, compared to those with unrestricted sleep just before. And a recent study 2020 published in theInternational Journal of Behavioral Medicinefound that "sleeping night before vaccination is critical", asShorter time shorter two days before vaccination leads to less antibodies in the following months.

Sleep plays a vital role in our immune system-Suner this as we rest. Therefore, less sleep means less time for your body to strengthen your immune response, which can make you more vulnerable to a series of diseases.
"People who sleep less than seven hours are three times more likely to be infected with rhinovirus or common rumier," Walker said at CNN. "We know that people who sleep five hours or less a night are 70% more likely to contract pneumonia."
Walker stated that additional research on the impact of sleep efficiency and vaccination could help in theCombat during coronavirus. He says it could be a "play changer" if there is a similar relationship between Sleep and COVD's successful vaccination because there is to sleep and vaccination against influenza.
Of course, the effectiveness of influenza vaccination is not the only thing that is affected by a lack of sleep. Read it to find out what other health problems can cause sleep deprivation and for more than the influenza season this year, discoverWhat could happen when Covid meets the flu.
1 Dementia

People who still have bad sleep tend to have higher concentrations of beta-amyloid proteins in their brain. According to a 2015 study published inNatureNeuroscience, this protein is associated with theDevelopment of dementia and Alzheimer's disease. And if you have trouble resting yourself,Never put this in your body before going to bed if you want to sleep, doctors say.
2 Colon Cancer

A 2011 study published in the newspaperCancerhas found that people with an average of less than six hours of sleep per night had a nearly 50%Increased risk of colorectal adenomas Compared to those who usually have seven hours of sleep or more each night. Colorectal adenomas are precursor lesions with colon cancer. And if you need an extra sleep, discover whichDays you should sleep to add years to your life.
3 Diabetes

A 2015 study published inDiabetic treatments found that for every hour less than seven hours, a person slept, they had 9%Increased risk of type 2 diabetes. This conclusion was collected from Harvard researchers, who analyzed 11 reports on the relationship between sleeping time and diabetes. And for no more night tips,That's exactly how much sleep you need to get, the study says.
4 Heart problems

The bad sleep can even affect your heart in different ways. In fact, disease control and prevention centers (CDC) warn less than seven hours per night puts you at greater risk of a heart attack . And for more information up to date, Sign up for our daily newsletter .


