If you have this type of blood, you are more likely to get blood clots
The research has established a link between this type of blood and the risk of blood coagulation.

Blood clots have been a major topic of discussions recently - mainly due to disease control and prevention centers (CDC) and the Food and Medicine Administration (FDA) decisionBreak the use of Johnson & Johnson's vaccine Due to an extremely rare but serious risk of blood clots in those who get shot. This side vaccine, there are other risk factors for the blood clots it deserves to be aware of. Depending on the search, your blood group can actually affect your chances of developing blood clots. Read on to find out what types of blood should pay particular attention to certain symptoms and for more risks by blood type,If you have this type of blood, your risk of cardiac attack is higher, the study says.
People with type B blood have the highest risk of blood clots.

Researchers have long sought to determine the link between the blood type and blood clotting - last recently in a study of 2020 January published inArteriosclerosis, thrombosis and vascular biology, American Heart Association Journal. Researchers in this study examined more than 400,000 people and found that those with blood B were the most likely tosuffer from blood coagulationAlso called thrombosis. In relation to type O blood, people with blood BB were 45% more likely to undergo thrombosis and 55% more likely to undergo deep vein thrombosis, which is a type of blood coagulation that occurs in his deep veins. And for recent news from the blood clot,Dr. Fauci says that anyone who got Johnson & Johnson Jab should do that.
And people with type o blood have the lowest risk of blood coagulation.
Type A blood is also at increased risk. In relation to type O blood, people with blood has had a higher thrombosis risk of 44% and an increased risk of 50% deep vein thrombosis. In fact, when examining any type of blood no o, relative to type O blood, there was a clear and significant increased risk. People with non-o type type were 44% more susceptible to thrombosis and 51% more likely to undergo deep vein thrombosis. They also had 47% more likely to develop a pulmonary embolism, which is where a lung travel clot.
"Our results are consistent with previous previous observation reports suggesting an increased risk of thromboembolic events in non-o blood group people, compared to blood group individuals O, explained the study. "In both blood groups A and B, we have observed similar risks to develop thromboembolic events compared to the blood group O." And for more useful information delivered directly in your inbox,Sign up for our daily newsletter.
This may be due to a difference in protein in the types of blood.
According to the study, there is an interesting link that can help explain the association between types of blood and blood clots. People with type o blood have a reduced amount of Von Willebrand Factor (VWF), a protein responsible for helping blood clots.
However, this is only a possible explanation. "Because thrombosis is a well-balanced and complex process, which is affected by a plethora of factors, there may be different biological mechanisms (cellular functionality, number of cell receptors) involved in the increased risk of thromboembolic events in the group Blood A and the people of blood B, in addition to the relationship already established with VWF, "concluded researchers in their study. And for more types of blood,If you have this type of blood, your risk of dementia is high, the study says.
If you encounter blood clotting symptoms, consult a doctor immediately.
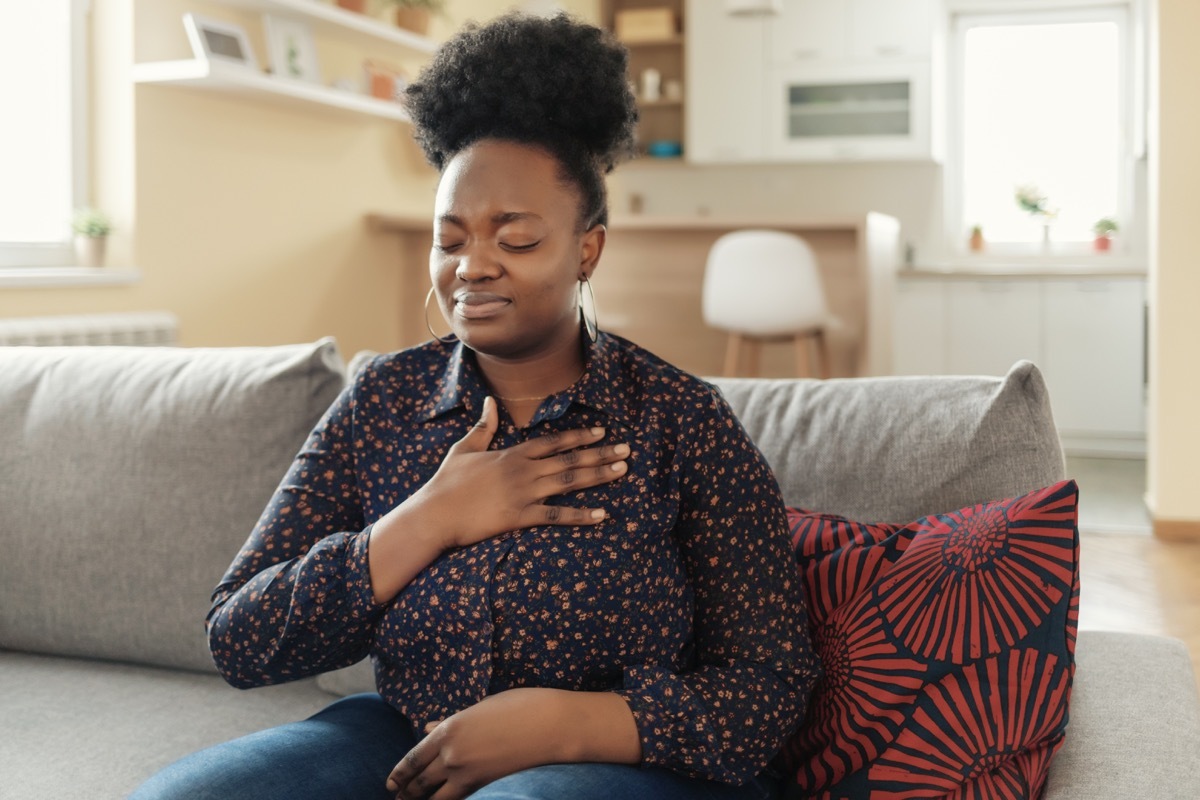

Know the signs and symptoms of blood clots is extremely important, likeMore than 100,000 people die each year Because of the blood clots, according to the CDC. The CDC says that you should know the symptoms of the two main types of blood coagulation: deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
For deep vein thrombosis, you can suffer swelling, pain, tenderness and redness of the skin in your arm, your leg or stomach - depending on where the blood clot. With a pulmonary embolism, you are likely to feel difficult to breathe, faster than the normal or irregular heart rate, the pain or discomfort of the chest, which usually worsens with deep breathing or coughing, coughing Blood and very low blood pressure, lightness and fainting. "If you have symptoms, consult your doctor as soon as possible," The CDC warns. And for more CDC advice, The CDC warns you to avoid this place, even if you are vaccinated .

Plumber finds hidden treasures of 75 years while renovating girls' toilets in an abandoned school

